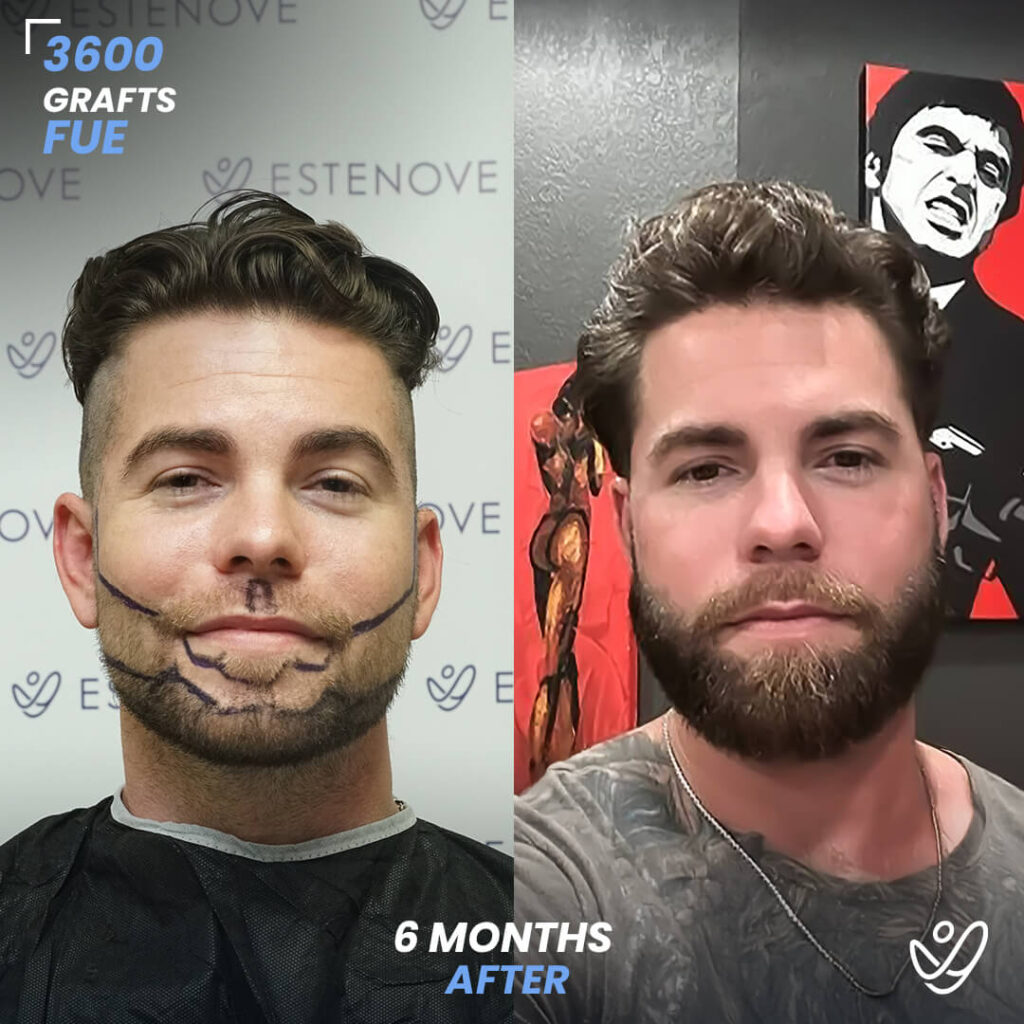
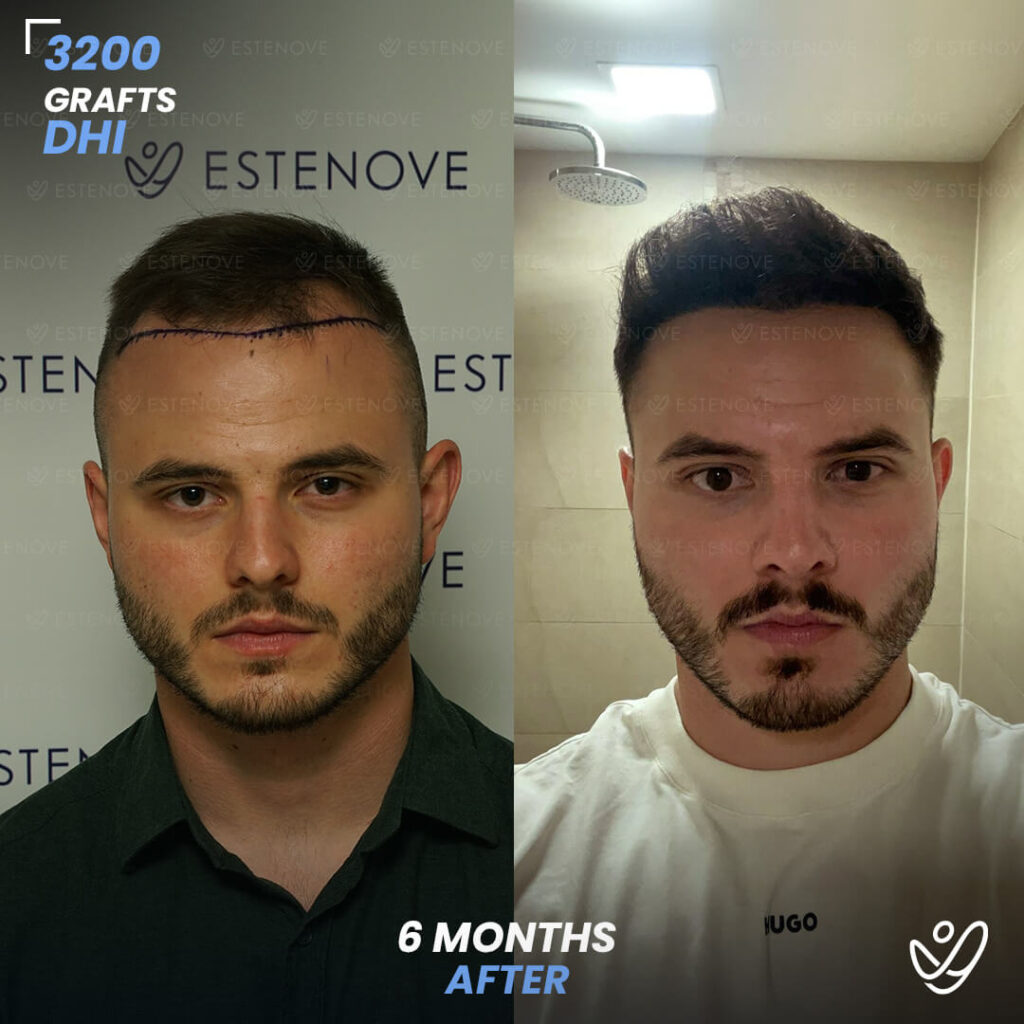
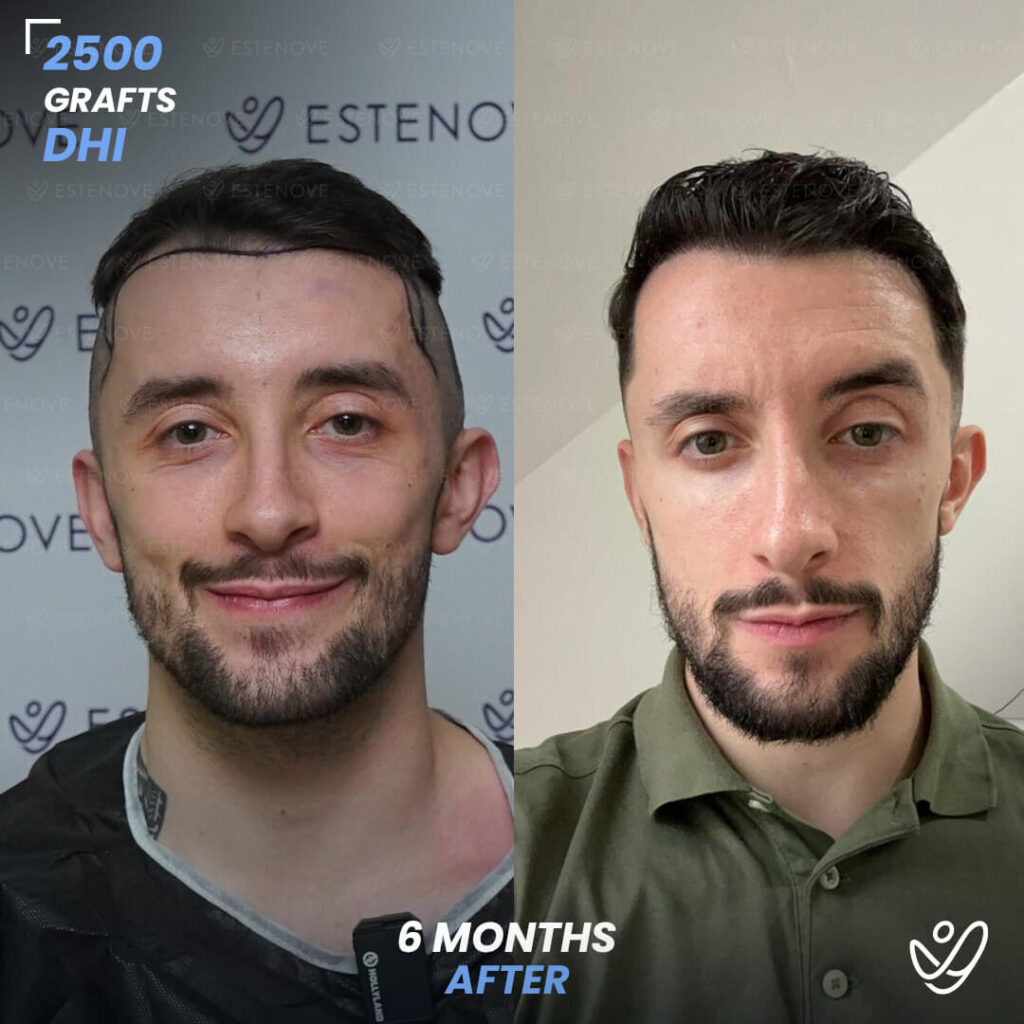
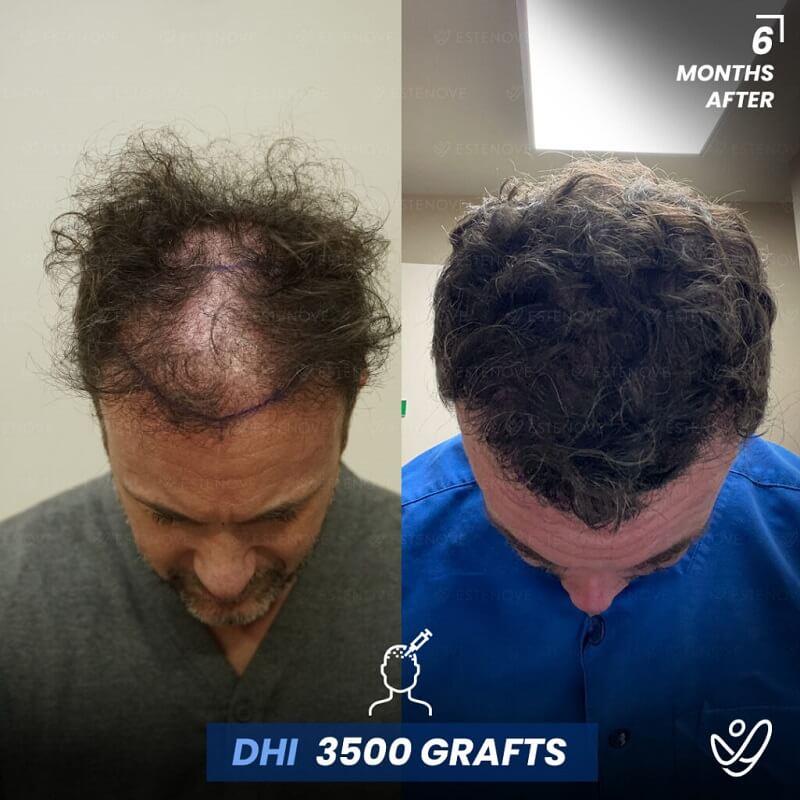
In today’s society, hair loss is a common concern that affects many individuals, particularly men. Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of hair loss in men. It typically follows a specific pattern and progresses over time. Understanding the Norwood-Hamilton Scale, the science behind male pattern baldness, and identifying its different stages are crucial in effectively addressing this issue. Additionally, exploring the factors contributing to male pattern baldness, lifestyle changes to combat hair loss, medical treatments, surgical options, and preventative measures can help individuals maintain healthy hair for longer.
Understanding the Norwood-Hamilton Scale
The Norwood-Hamilton Scale is a classification system widely used by medical professionals to determine the extent of hair loss in individuals with male pattern baldness. This scale helps identify the severity of the condition and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Consulting a hair specialist or dermatologist who can assess your hair loss using the Norwood-Hamilton Scale is crucial for understanding the stage of hair loss and exploring suitable treatment options.
First introduced by Dr. James Hamilton in the 1950s and later modified by Dr. O’Tar Norwood in the 1970s, the Norwood-Hamilton Scale consists of seven stages that depict the progression of male pattern baldness. Stage I represents minimal to no hair loss, while Stage VII indicates the most advanced stage with significant hair loss across the crown and front of the head.
It is important to note that the Norwood-Hamilton Scale focuses specifically on male pattern baldness and may not be applicable to other types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata or telogen effluvium. Understanding where you fall on the scale can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about potential treatment options.
The Science Behind Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness is primarily caused by genetic factors and hormonal imbalances. It is typically inherited through non-sex-linked genetic inheritance from both the mother and father. The main hormone involved is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, which binds to specific receptors in hair follicles, miniaturizing them over time.
In individuals with a genetic predisposition to male pattern baldness, the hair follicles become more sensitive to DHT, leading to a gradual shrinking of the follicles, shorter hair production cycles, and thinner hair strands. This process eventually leads to the complete cessation of hair growth from affected follicles.
Research has shown that male pattern baldness is not solely determined by genetics. Environmental factors such as stress, diet, and lifestyle choices can also play a role in the onset and progression of hair loss. Chronic stress, for example, can trigger hormonal changes in the body that may exacerbate the effects of DHT on hair follicles.
Furthermore, studies have indicated a potential link between male pattern baldness and certain medical conditions such as prostate cancer and cardiovascular disease. The presence of male pattern baldness has been suggested as a possible marker for these conditions, although more research is needed to establish a definitive connection.
Identifying the Different Stages of Hair Loss
The Norwood-Hamilton Scale consists of various stages that indicate the progression of male pattern baldness. These stages range from minimal hair loss to extensive baldness. It is essential to identify the stage of hair loss accurately to determine the most suitable treatment options.
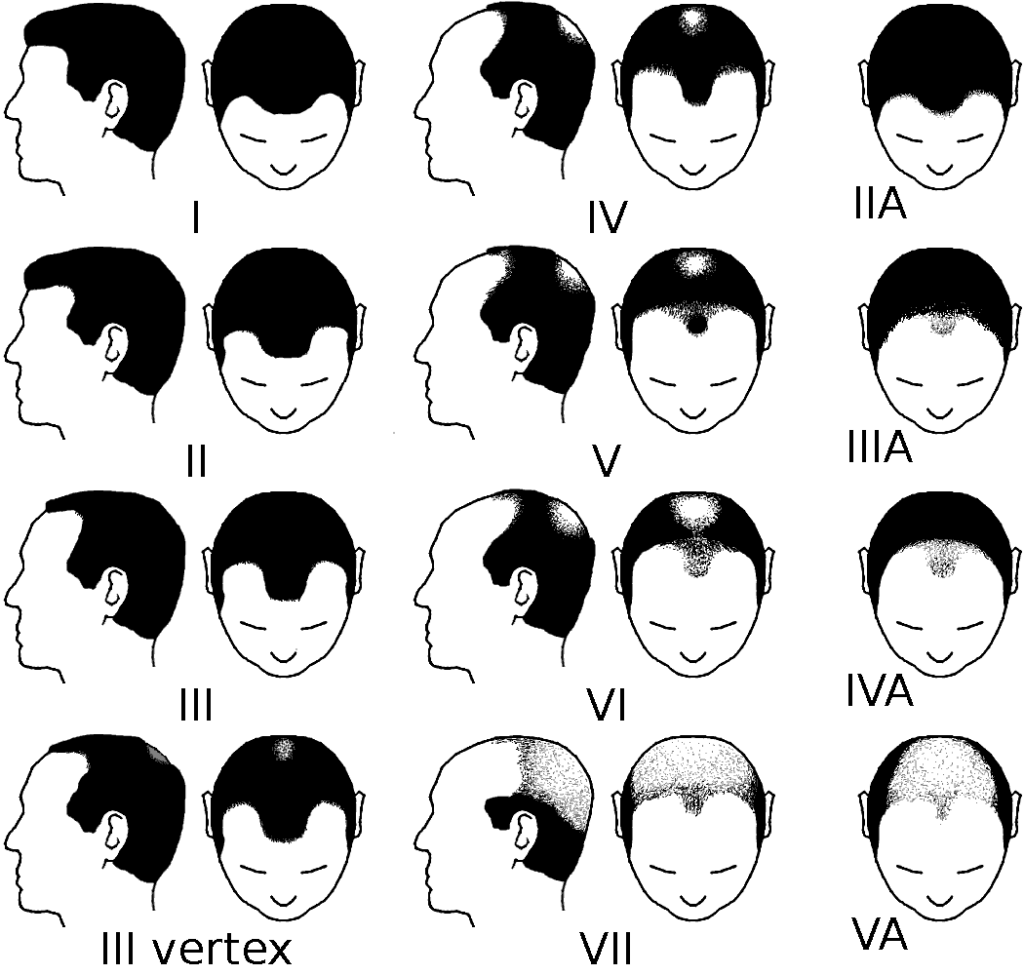
Norwood scale for male pattern baldness, Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamilton%E2%80%93Norwood_scale
Stage 1 represents the absence of significant hair loss, while stage 7 indicates severe hair loss, leaving only a strip of hair around the sides and back of the head. The stages in between gradually depict the increasing extent of hair loss and the affected areas, such as the hairline, crown, or both.
Stages of the Norwood-Hamilton Scale
Stage I: This stage is characterized by minimal or no recession of the hairline.
Stage II: There is a slight recession of the hairline around the temples. This is often referred to as an adult or mature hairline.
Stage III: The first signs of clinically significant balding appear. There is a deep symmetrical recession at the temples that are bare or just sparsely covered by hair.
Stage IV: Hairline recession is more severe than in stage III, and there is sparse hair or no hair on the vertex. The two areas of hair loss are separated by a band of hair that connects to the hair remaining at the sides of the scalp.
Stage V: The areas of hair loss are larger than in stage IV. They are still separated, but the band of hair between them is narrower and sparser.
Stage VI: The bridge of hair that once separated the front and the back is gone or sparse, and the bald areas at the front and back join together.
Stage VII: The most severe stage of hair loss, only a band of hair going around the sides of the head remains. This hair is usually not dense and may be fine.
Factors Contributing to Male Pattern Baldness
While genetics and hormonal imbalances play a significant role in male pattern baldness, several other factors can contribute to the condition’s progression. Stress, poor nutrition, smoking, and underlying medical conditions such as thyroid disorders can accelerate hair loss.
Identifying these factors and addressing them can help slow down hair loss or even prevent it from worsening. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress levels, and ensuring a balanced diet can positively impact hair health.
In addition to lifestyle factors, environmental influences can also play a role in male pattern baldness. Exposure to pollutants, UV radiation, and harsh chemicals in hair products can weaken hair follicles and contribute to hair loss. It is important to protect your hair from these external stressors to maintain its health and vitality.
Furthermore, age is another significant factor in male pattern baldness. As men grow older, the hair growth cycle can slow down, leading to thinner and weaker hair. Understanding the natural aging process of hair can help individuals better manage their expectations and take proactive steps to care for their hair as they age.
Lifestyle Changes to Combat Hair Loss
Implementing certain lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to maintaining healthy hair and reducing the progression of male pattern baldness. Regular exercise not only improves blood circulation to the scalp but also helps in reducing stress levels, which can be a contributing factor to hair loss. Incorporating activities like yoga or meditation into your routine can further aid in stress management, promoting overall scalp health.
Using mild shampoos is essential to prevent stripping the hair of its natural oils, which can lead to dryness and breakage. Avoiding excessive heat styling tools such as flat irons and curling wands can also help in preserving the integrity of the hair strands. Furthermore, limiting the use of chemical products like hair dyes and relaxers can reduce the risk of damage to the hair follicles, promoting healthier hair growth in the long run.
When it comes to diet, consuming foods rich in essential nutrients is crucial for maintaining optimal hair health. Vitamins A, B, C, and E play key roles in promoting hair growth and strengthening the hair shaft. Minerals like zinc and iron are also vital for maintaining healthy hair follicles and preventing hair loss. Including a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins in your diet can provide the necessary building blocks for strong and vibrant hair.
Medical Treatments for Male Pattern Baldness
For individuals seeking medical intervention, various treatments are available to address male pattern baldness. These treatments aim to slow down hair loss, stimulate hair growth, and improve overall hair density.
Topical medications such as minoxidil, also known as Rogaine, can be applied directly to the scalp to promote hair growth. This over-the-counter treatment is commonly recommended for its ability to widen hair follicles and prolong the hair growth phase. Additionally, minoxidil is available in different strengths, with higher concentrations typically yielding more noticeable results.
Prescription medications like finasteride, commonly known as Propecia, work internally to inhibit the conversion of testosterone to DHT, effectively reducing hair loss. By targeting the root cause of male pattern baldness, finasteride can help maintain existing hair and even promote new growth in some individuals. It is important to note that finasteride may take several months to show visible effects, and continuous usage is usually required to sustain results.
Aside from topical and oral medications, another emerging treatment for male pattern baldness is low-level laser therapy (LLLT). This non-invasive procedure involves using red light wavelengths to stimulate hair follicles, potentially increasing blood flow and nutrient delivery to the scalp. LLLT devices come in various forms, including laser caps and combs, offering convenience for users looking to incorporate this therapy into their daily routine.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before initiating any medical treatments to assess their suitability and potential side effects. Understanding the mechanisms of action and expected outcomes of these treatments can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their hair loss management.
Surgical Options for Hair Restoration
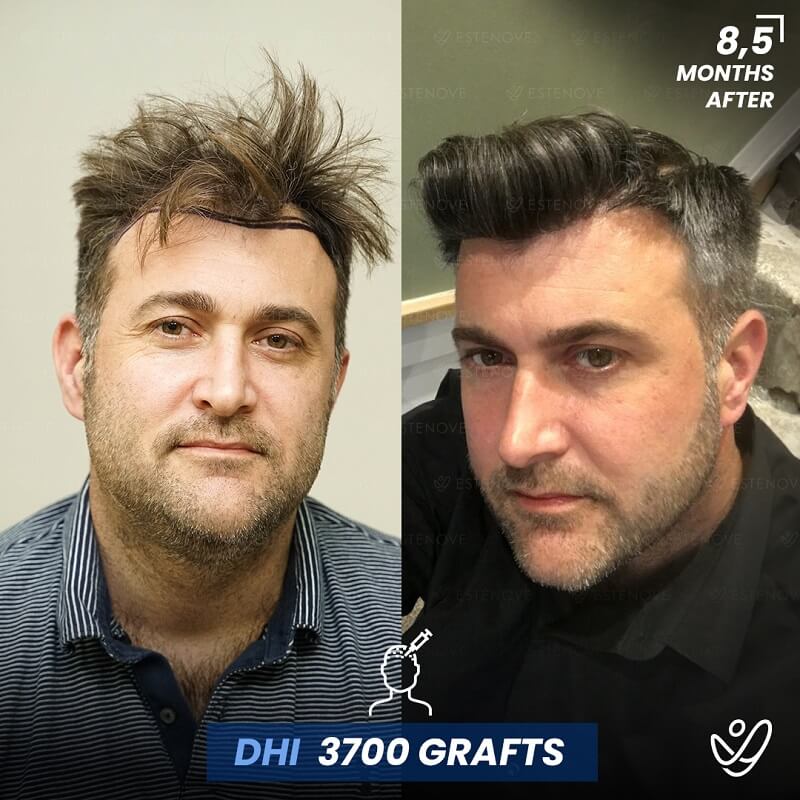
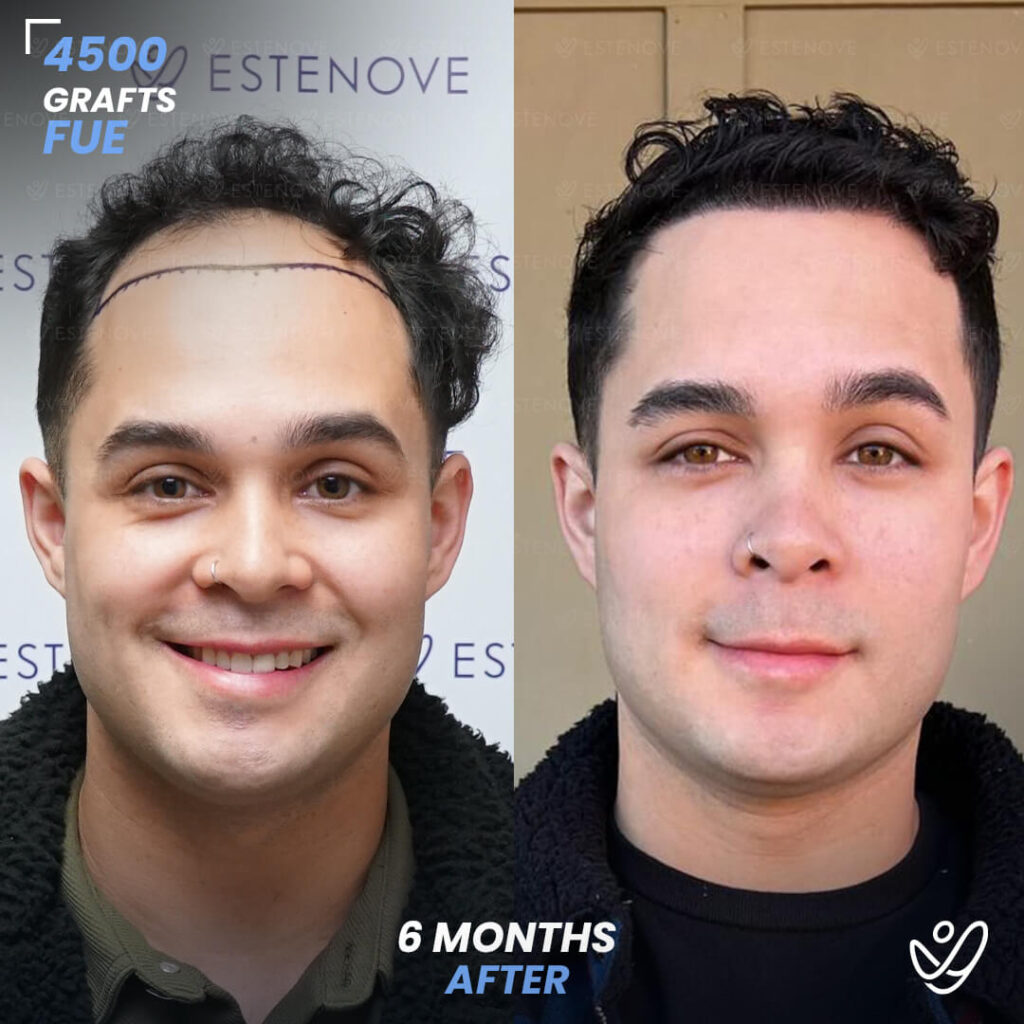
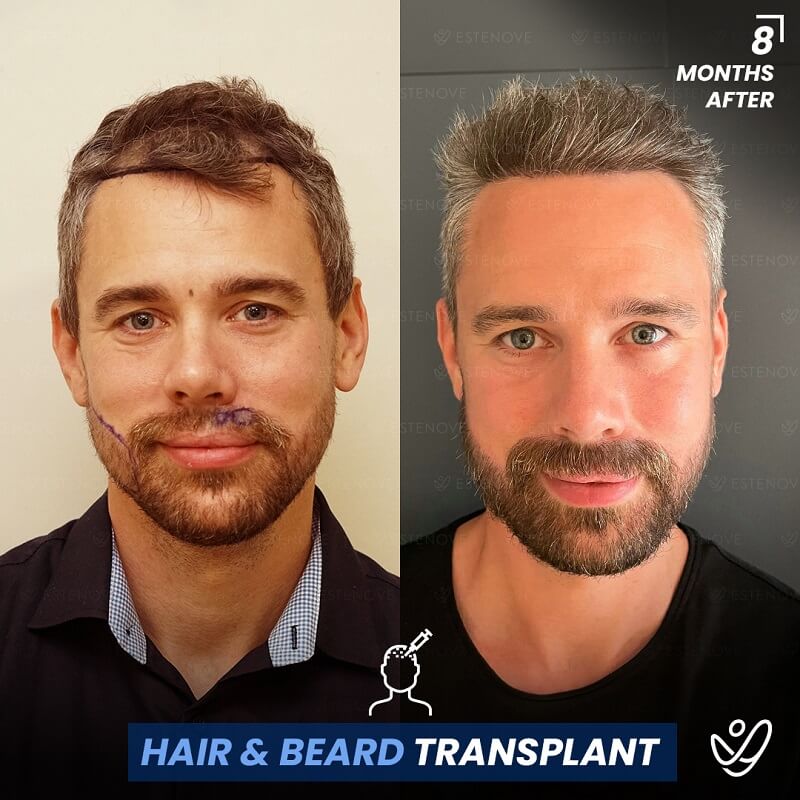
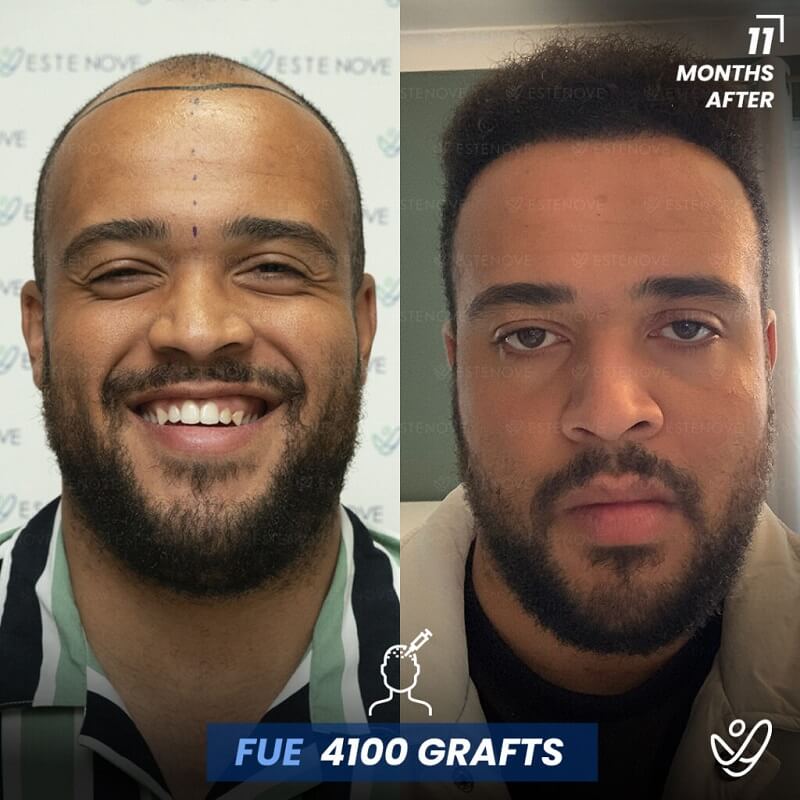
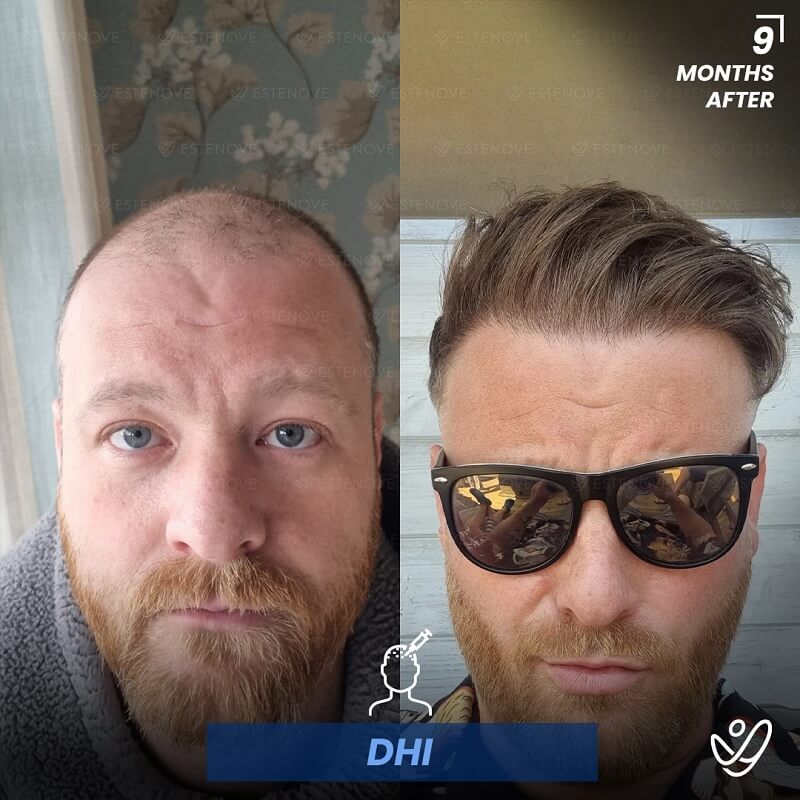
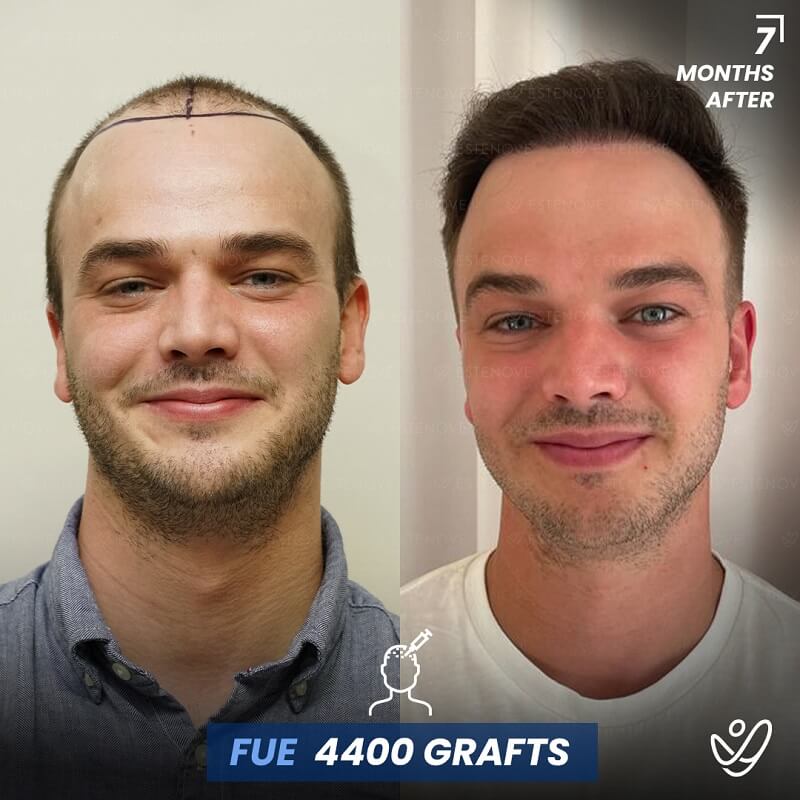
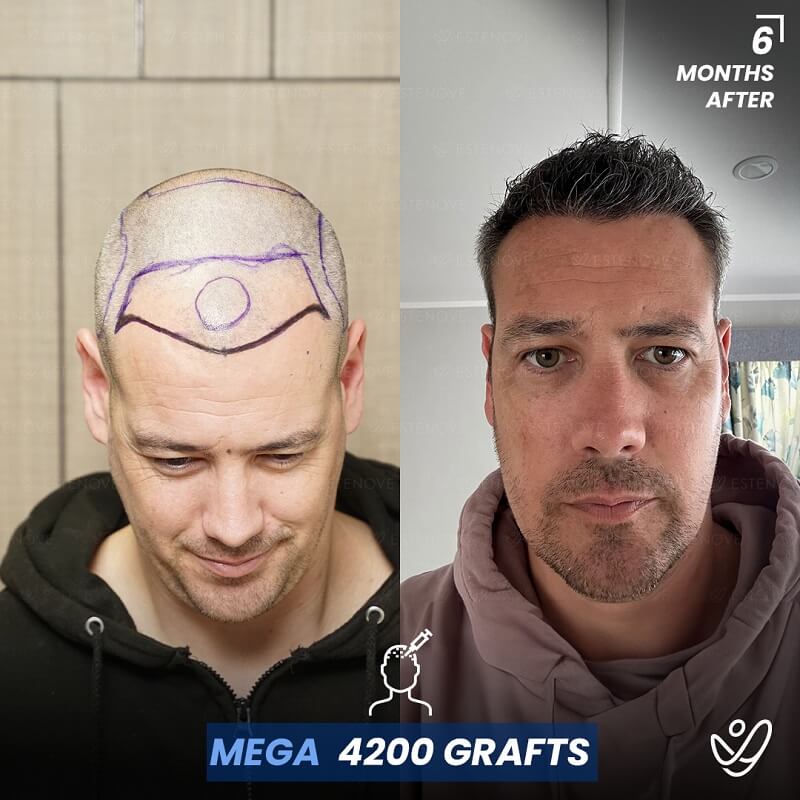
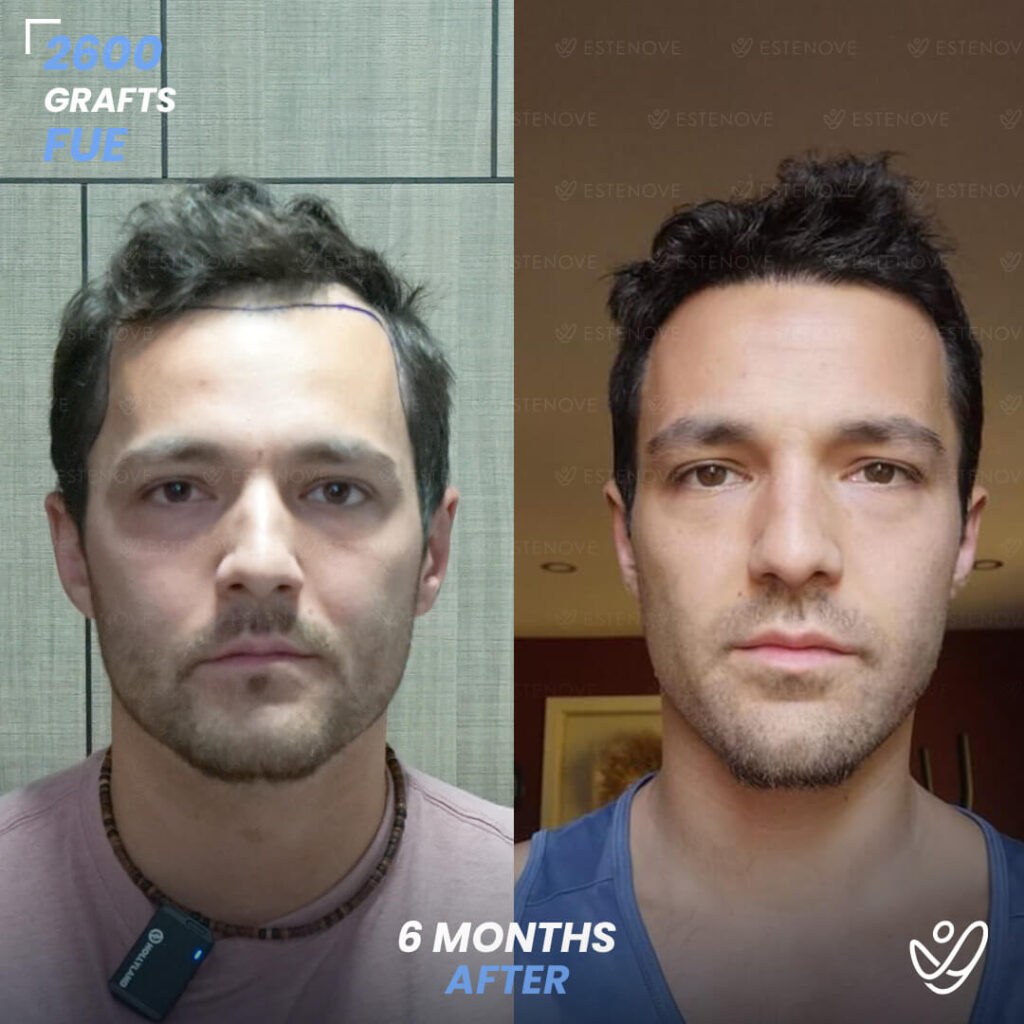
In cases where non-surgical treatments are ineffective or individuals desire a more significant transformation, surgical options for hair restoration can be considered. Hair transplant procedures, such as follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit transplantation (FUT), involve relocating hair follicles from donor areas to areas experiencing hair loss.
Calculate the number of grafts needed for your hair transplant and get an estimated cost for various destinations. Try graft calculator
These procedures provide long-lasting results for getting your hair back and natural-looking hair growth. However, it is essential to consult with a qualified hair transplant surgeon to determine candidacy and discuss the details of the procedure.
Fill the form below to get free consultation
Preventative Measures to Maintain Healthy Hair
Prevention plays a vital role in maintaining healthy hair and minimizing the impact of male pattern baldness. Regular scalp massages can improve blood circulation, ensuring a healthy environment for hair follicles. Protecting the scalp from excessive sun exposure and avoiding harsh treatments and hairstyles can also prevent hair damage.
Additionally, maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is essential for healthy hair growth. Adequate hydration and stress management techniques are equally important in promoting scalp and overall hair health.
Furthermore, starting preventive measures at the early stages of hair loss can significantly slow down the progression of male pattern baldness and preserve a fuller head of hair for longer.
– – –
Understanding the Norwood-Hamilton Scale and the science behind male pattern baldness provides insights into the stages of hair loss and facilitates the development of appropriate treatment plans. Factors like genetics, hormonal imbalances, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions contribute to male pattern baldness. By embracing lifestyle changes, exploring medical treatments, considering surgical options, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can effectively address hair loss and maintain healthier hair.