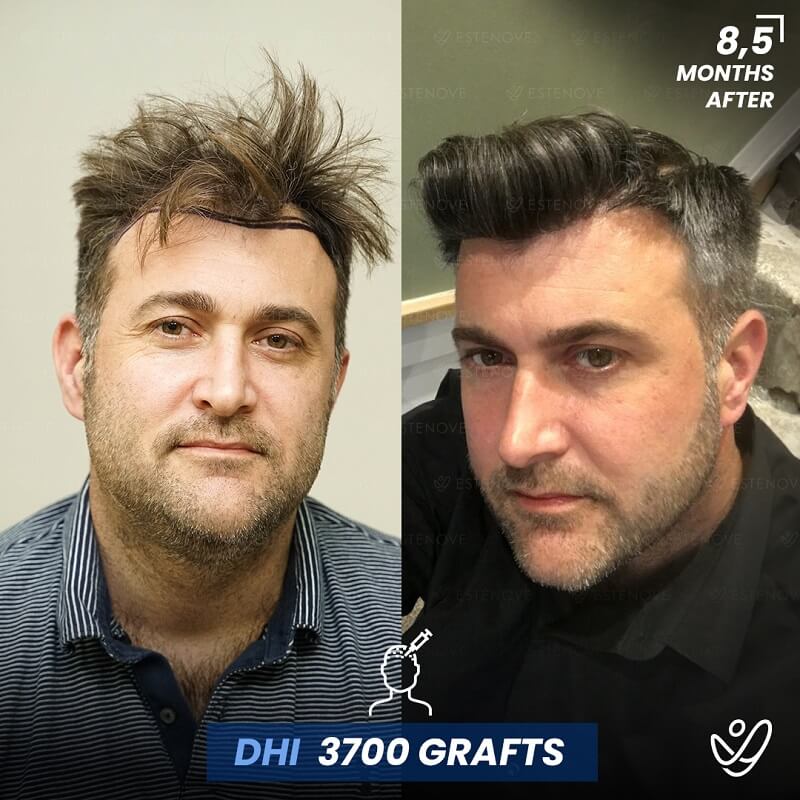
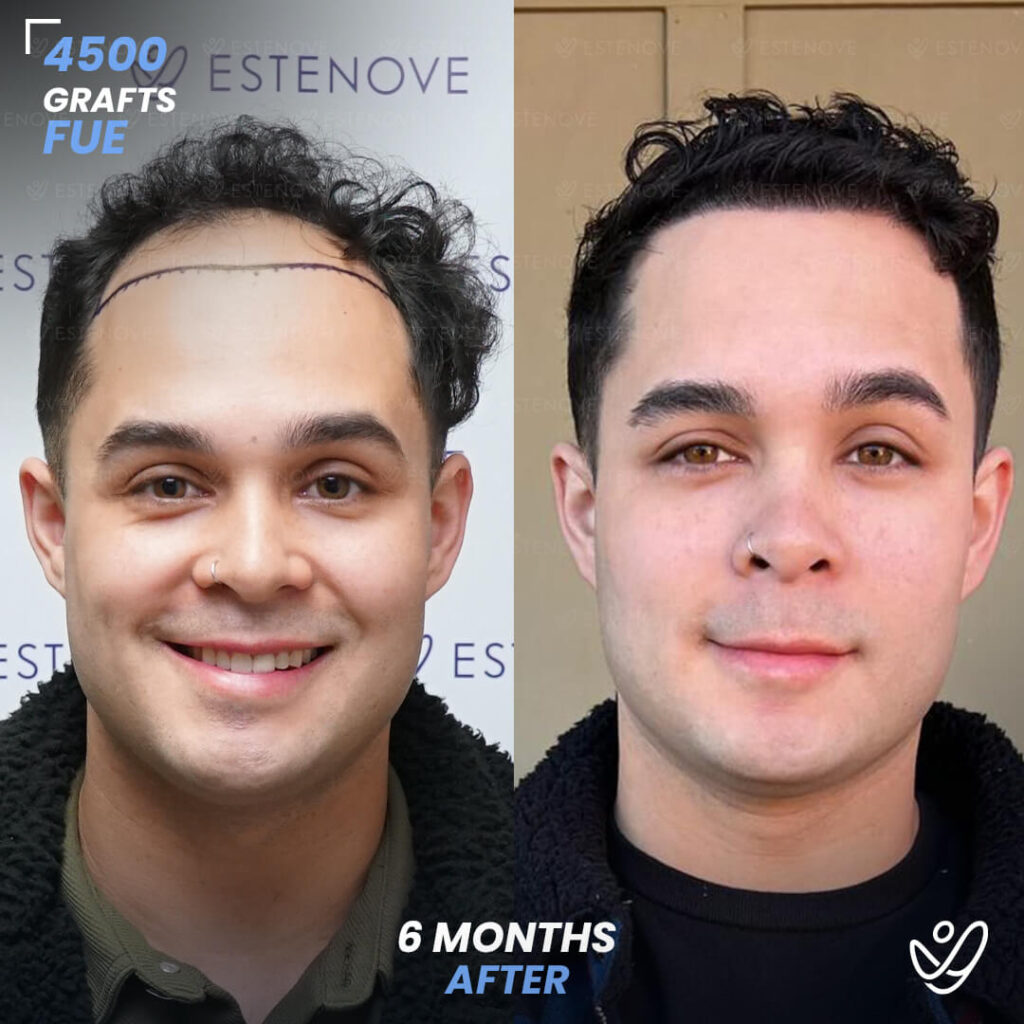
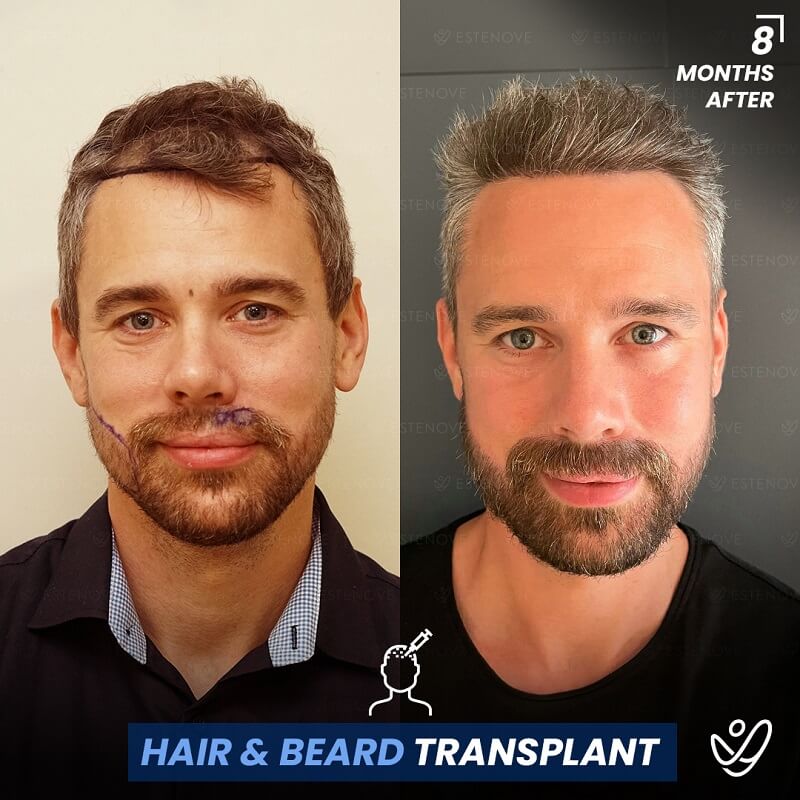
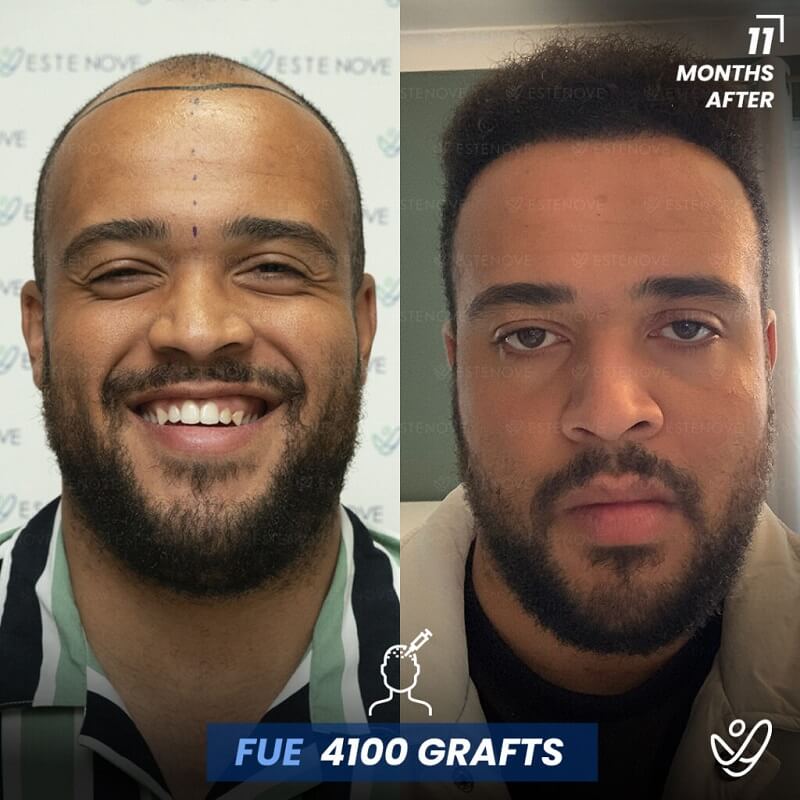
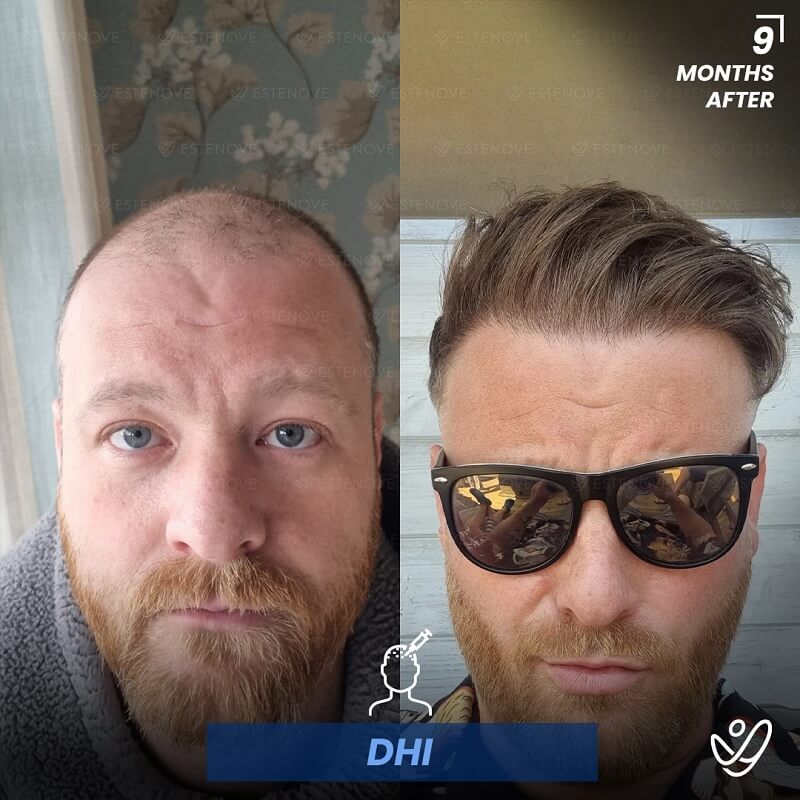
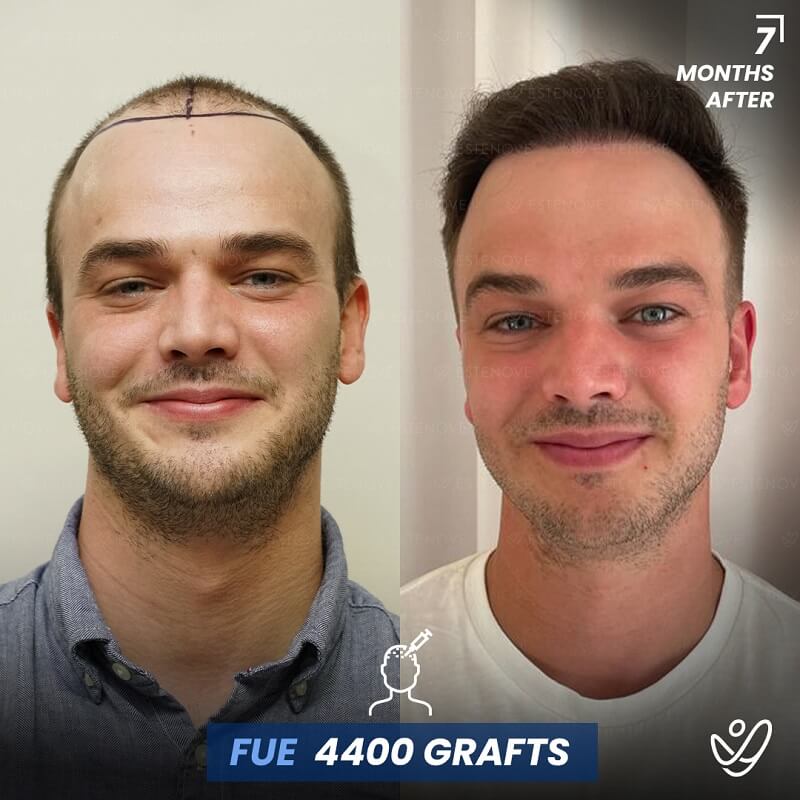
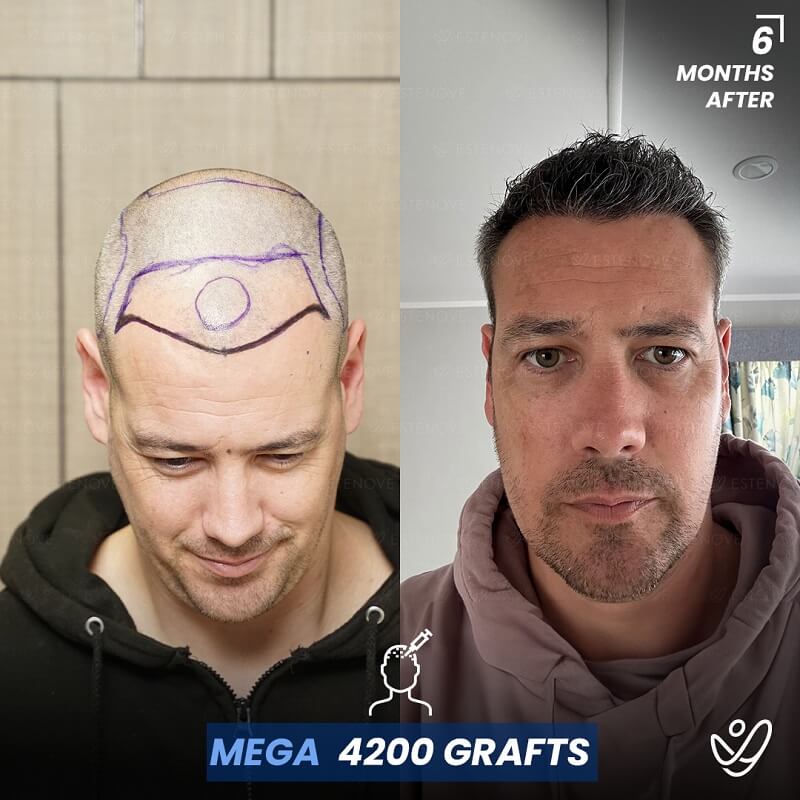
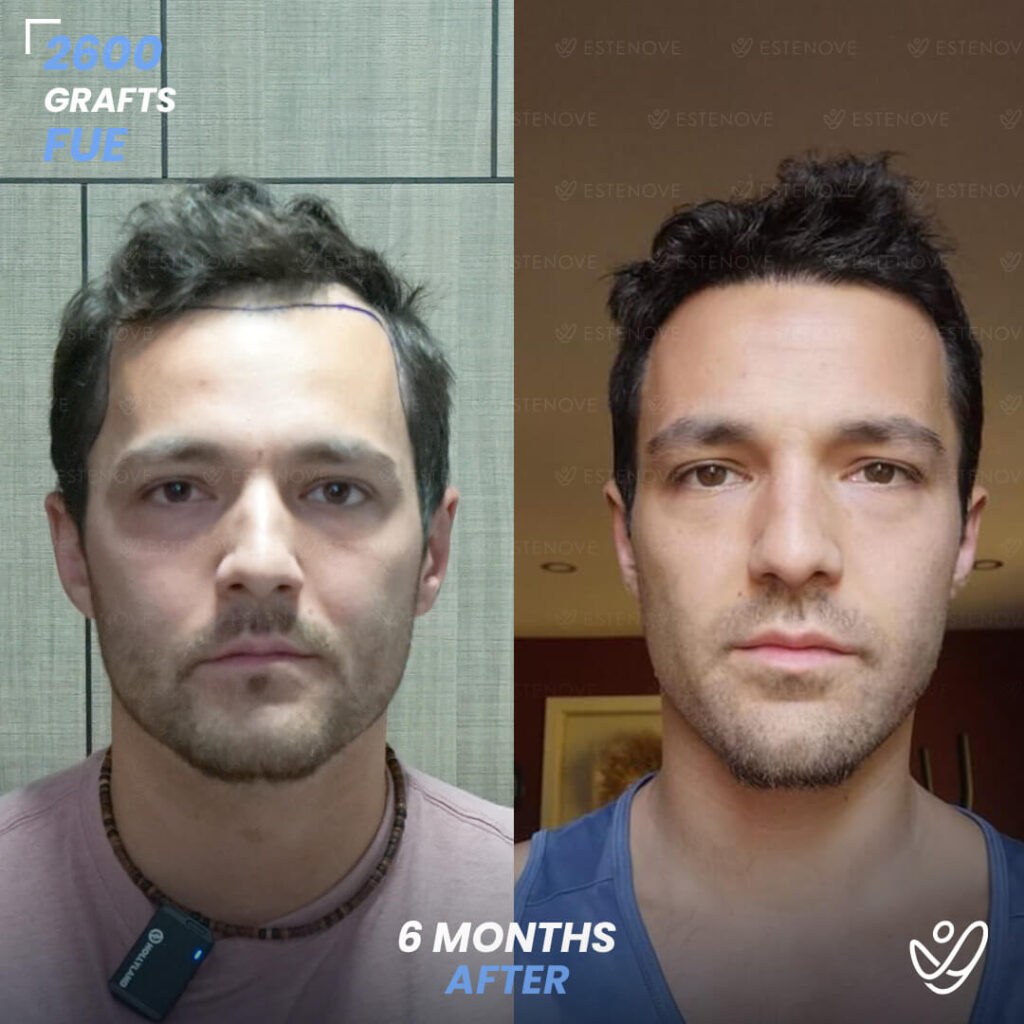
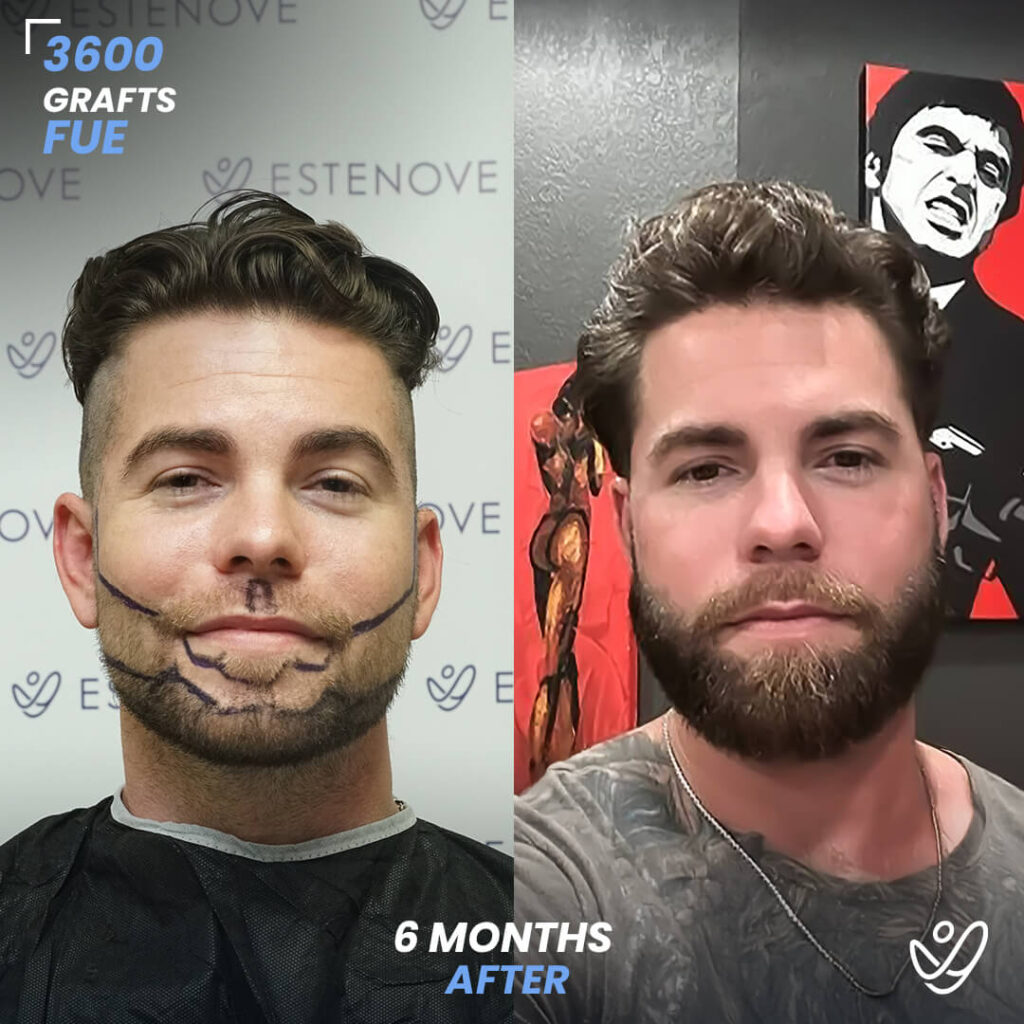
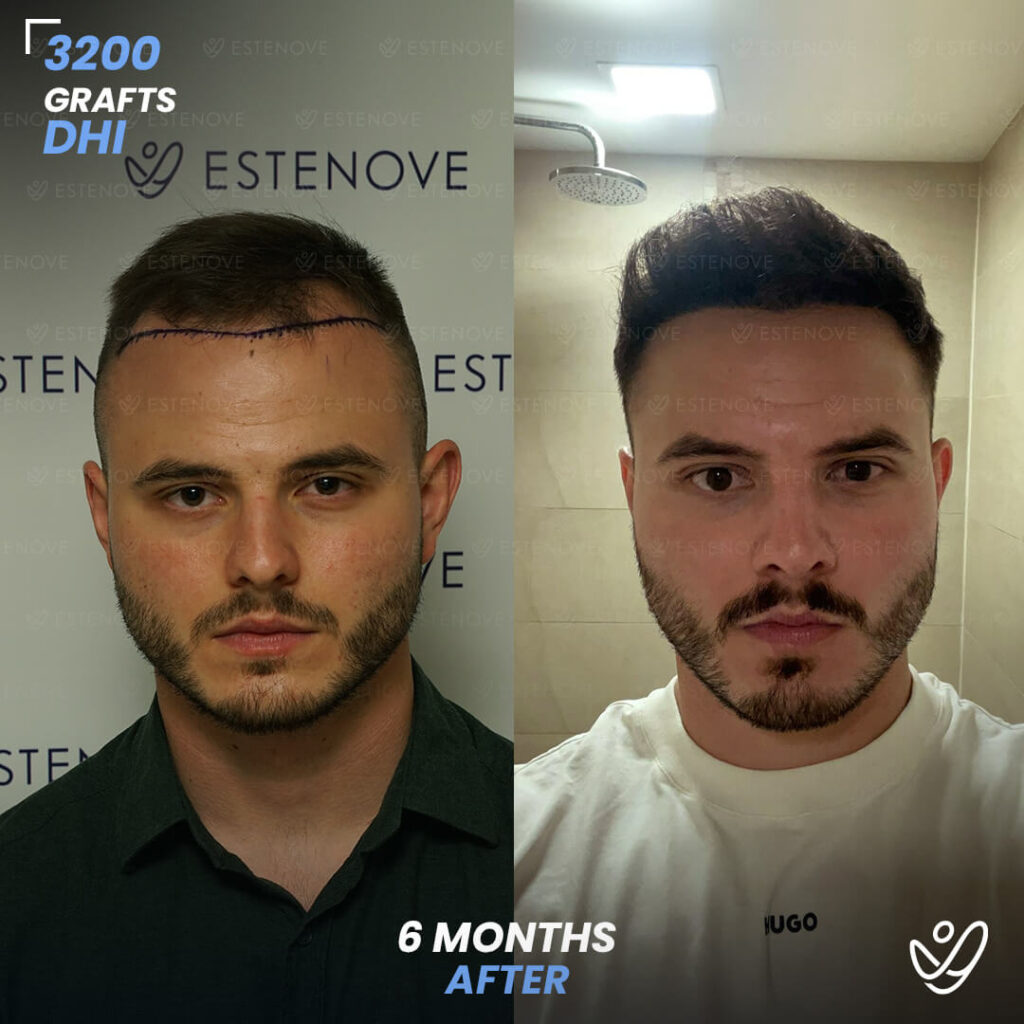
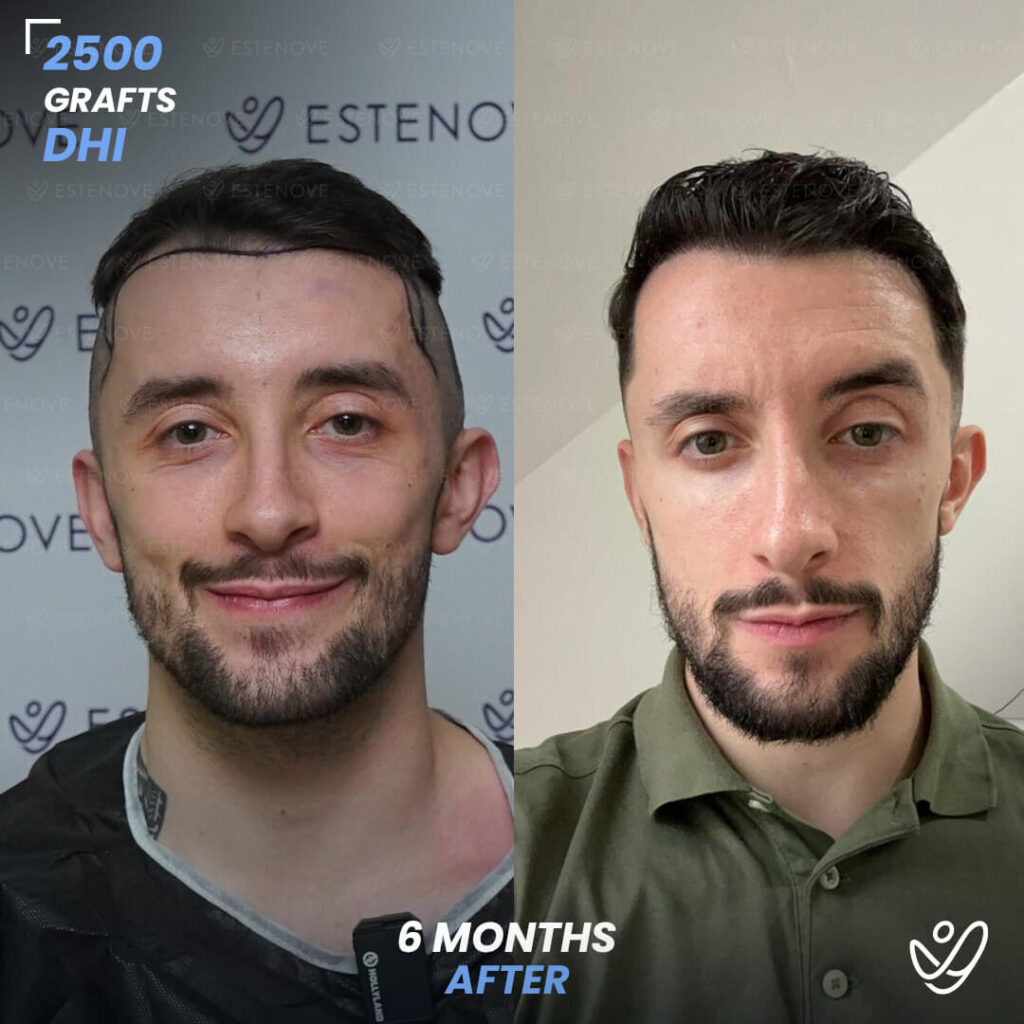
What is Hair Follicle?
The hair follicle is a small, complex structure that plays a vital role in the growth and maintenance of hair. Knowing the anatomy and function of hair follicles can help us better understand common hair problems and how to address them. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of hair follicles, from their life cycle to disorders and treatments, hormonal influences, hair loss, regeneration, and techniques for stimulating faster hair growth.
Understanding the Anatomy of Hair Follicles
Before we delve into the complexities of hair follicles, let’s start with their basic anatomy. Hair follicles are tiny, tube-like structures located in the skin. Each follicle has two main components: the hair shaft and the hair bulb. The hair bulb, situated at the base of the follicle, contains special cells responsible for hair growth. The hair shaft, on the other hand, is the visible part of the hair that extends beyond the skin surface.
Within the hair follicle, there are different layers that contribute to its function. The innermost layer, known as the dermal papilla, plays a crucial role in supplying nutrients to the growing hair. The dermal papilla is a small, highly vascularized structure that is responsible for nourishing the hair follicle and supporting its growth. It contains a rich network of blood vessels that deliver oxygen and nutrients to the hair cells, ensuring their proper development and functioning.
The outer layer of the hair follicle, called the dermal sheath, surrounds the follicle and provides structural support. It is composed of connective tissue and plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity and stability of the hair follicle. The dermal sheath also contains specialized cells that are involved in the production of hair pigments, giving hair its color.
Another important component of the hair follicle is the sebaceous gland. This gland is attached to the side of the follicle and produces sebum, an oily substance that lubricates and protects the hair and the surrounding skin. Sebum helps to keep the hair moisturized and prevents it from becoming dry and brittle.
Additionally, the hair follicle is surrounded by a network of nerves and blood vessels, which provide sensory and circulatory support. These blood vessels supply oxygen and nutrients to the hair follicle, while the nerves transmit signals to and from the hair follicle, allowing for sensory perception and regulation of hair growth.
In summary, the hair follicle is a complex structure with various components that work together to support hair growth and maintenance. Understanding the anatomy of hair follicles is essential for comprehending the processes involved in hair growth, as well as for developing effective strategies for hair care and treatment.
The Life Cycle of Hair Follicles: Growth, Rest, and Shedding
Understanding the life cycle of hair follicles can shed light on why our hair goes through different phases and what we can expect in terms of growth and shedding. The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen.
In the anagen phase, which lasts for several years, the hair actively grows from its bulb at the base of the follicle. This is the phase that determines the length of our hair. During this phase, the hair follicle is in a state of high activity, with cells dividing rapidly and producing new hair cells. The hair strand grows approximately half an inch per month, and the length it reaches during the anagen phase is largely determined by genetics and individual factors such as diet and overall health.
After the anagen phase, the catagen phase follows, where the hair stops growing and transitions into a resting phase. This phase lasts for a relatively short period of time, typically around two to three weeks. During the catagen phase, the hair follicle undergoes structural changes, with the lower part of the hair strand detaching from the blood supply and the cells in the hair bulb shrinking. This transition prepares the hair follicle for the next phase of the cycle.
Finally, the telogen phase begins, during which the hair follicle prepares to shed the hair strand and enter a new growth cycle. This phase lasts for about three to four months. While the hair strand is in the telogen phase, it is no longer actively growing. Instead, it remains attached to the hair follicle but is held in place by a club-shaped structure. This club-shaped structure is formed by the lower part of the hair strand that detached during the catagen phase. During the telogen phase, a new hair strand begins to form in the hair bulb, signaling the start of a new growth cycle.
It’s important to note that each hair follicle operates independently, meaning that hairs are in different phases of the growth cycle at any given time. This is why we experience a mix of growing, resting, and shedding hairs on our scalp. On average, about 85% of our hair follicles are in the anagen phase, 1-2% are in the catagen phase, and 10-15% are in the telogen phase. This constant turnover of hair follicles ensures that we have a continuous supply of new hair strands.
Various factors can influence the duration of each phase and the overall hair growth cycle. For example, hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can affect the length of the anagen phase. Additionally, certain medical conditions, medications, and nutritional deficiencies can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, leading to excessive shedding or hair loss.
Understanding the intricacies of the hair growth cycle can help us better care for our hair. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and proper hair care practices, we can support the optimal functioning of our hair follicles and promote healthy hair growth. Additionally, being aware of the natural shedding and regrowth process can help alleviate concerns about temporary hair loss and provide reassurance that new hair strands will replace the ones that are shed.
Common Hair Follicle Disorders and How to Treat Them
Various factors can disrupt the normal functioning of hair follicles, resulting in different hair follicle disorders. Some common disorders include alopecia areata, folliculitis, and hirsutism.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Folliculitis, on the other hand, is an infection of the hair follicles caused by bacteria or fungi. Hirsutism refers to excessive hair growth in areas where it is typically minimal, such as the face and chest in women.
Treatment for hair follicle disorders depends on the specific condition. It may include topical medications, oral medications, laser therapy, or surgical interventions. Consulting with a dermatologist is crucial for accurate diagnosis and customized treatment plans.
The Role of Hormones in Hair Follicle Health
Hormones play a significant role in the health and function of hair follicles. Androgens, a group of male sex hormones, can affect hair growth in both men and women. In conditions like androgenetic alopecia, the sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens increases, leading to hair thinning and eventual loss.
Other hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid dysfunction or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can also impact hair follicles and result in hair thinning or excessive hair growth. Diagnosing and addressing these hormonal imbalances is essential for maintaining optimal hair follicle health.
Exploring the Connection Between Hair Follicles and Hair Loss
Hair loss is a common concern for many individuals, and understanding its link to hair follicles can provide valuable insights. Hair loss can occur due to various reasons, including genetics, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions.
In individuals predisposed to hair loss, hair follicles become more sensitive to hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), leading to a shortening of the hair growth cycle and eventual hair thinning. Over time, this can progress to baldness in some cases.
While some forms of hair loss are irreversible, early intervention and appropriate treatments can slow down the process and promote healthier hair growth. Options range from medications (such as minoxidil or finasteride) to hair transplant surgery, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the hair loss.
The Science Behind Hair Follicle Regeneration and Restoration
Advancements in scientific research have opened up possibilities for hair follicle regeneration and restoration. Researchers are exploring methods to stimulate dormant hair follicles, awaken stem cells within the follicles, and promote new hair growth.
One promising avenue in this field is stem cell therapy, where stem cells are injected into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair growth. Other techniques involve the use of growth factors, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which contain concentrated substances that promote cellular growth and healing.
While hair follicle regeneration and restoration techniques are still in their early stages, they offer hope for individuals experiencing hair loss and may pave the way for more effective treatment options in the future.
How to Stimulate Hair Follicles for Faster Hair Growth
Boosting hair follicle health can contribute to faster hair growth and improved hair quality. Several natural and lifestyle factors can enhance hair follicle stimulation:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals that support hair growth
- Regular scalp massage to increase blood circulation and nourish the hair follicles
- Avoiding excessive heat styling and chemical treatments that can damage the hair follicles
- Reducing stress levels, as stress can impact hair growth and follicle function
- Using hair care products specifically formulated to nourish and strengthen the hair follicles
Remember, stimulating hair follicles for faster hair growth is a journey that requires patience and consistency. Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can support overall hair health and potentially enhance hair growth.
Understanding the complexities of hair follicles is crucial for maintaining healthy hair and addressing common hair problems. By exploring the anatomy, life cycle, disorders, hormonal influences, hair loss, regeneration potential, and stimulation techniques, we gain valuable insights into the science behind our hair. With proper care and knowledge, we can optimize hair follicle health and promote the growth of luscious, vibrant locks.
Sources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hair_follicle, Last access 22.04.2024