Finasteride is an oral medication primarily used to treat male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. By inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, finasteride decreases the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Elevated levels of DHT have been linked to shrinking hair follicles and subsequent hair loss.
Table of Contents
- Finasteride for Hair Loss: How It Works
- The Science Behind Hair Regrowth: What Studies Show
- Who Can Benefit from Finasteride Treatment?
- Potential Side Effects of Finasteride: What to Expect
- When to Expect Hair Regrowth with Finasteride
- Comparing Finasteride with Other Hair Loss Treatments
- Dosage and Administration: How to Use Finasteride Effectively
- Myths and Misconceptions About Finasteride
- Evaluating Options: Hair Transplant vs Medications
- Consulting a Professional: When to Seek Medical Advice
Finasteride for Hair Loss: How It Works
The drug binds to the enzyme, which reduces the levels of DHT in the scalp and encourages hair regrowth in men who are experiencing thinning hair. Though finasteride does not work for everyone, many clinical studies have evidenced its effectiveness in promoting hair growth and preventing further loss.
In addition to its primary use in treating hair loss, finasteride has also been studied for its potential benefits in other areas, such as reducing the risk of prostate cancer. Research indicates that lower DHT levels may contribute to a decreased incidence of certain prostate conditions, making finasteride a dual-purpose medication for some men. However, it is crucial for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider, as finasteride can also lead to side effects, including sexual dysfunction and mood changes, which may impact the quality of life.
Moreover, the timeline for seeing results from finasteride can vary significantly among individuals. While some may notice improvements in hair density within a few months, others might take up to a year to see substantial changes. This variability can be attributed to factors such as genetics, the severity of hair loss, and adherence to the medication regimen. For those considering finasteride, it is essential to maintain realistic expectations and to combine the treatment with a healthy lifestyle, which includes a balanced diet and regular exercise, to maximize the potential benefits for hair restoration.
The Science Behind Hair Regrowth: What Studies Show
Numerous studies have assessed the efficacy of finasteride for hair loss. One large-scale trial showed that approximately 83% of participants experienced moderate to significant improvement after 12 months of treatment. This suggests that finasteride effectively stabilizes hair loss and induces regrowth in a substantial number of men.
Furthermore, research indicates that the benefits of finasteride often continue for as long as it is taken. A follow-up extension study noted that most men maintained or improved their hair density even after two years of use. This growing body of evidence solidifies finasteride’s role as a cornerstone in the management of male pattern baldness.
Who Can Benefit from Finasteride Treatment?
Finasteride is ideally suited for adult men experiencing early signs of hair loss. The medication is typically prescribed to men aged 18 to 41, especially those with mild to moderate thinning at the crown or front of the scalp. However, not everyone is a suitable candidate.
Women, especially those who are pregnant or may become pregnant, are advised against using finasteride due to the risk of birth defects. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications should consult with a healthcare provider before initiating treatment.
Potential Side Effects of Finasteride: What to Expect
While many men tolerate finasteride well, some may experience side effects. Common side effects include sexual dysfunction, such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation disorders.¹ These effects can vary in severity and may resolve after discontinuation of the drug.
Less common side effects include breast tenderness or enlargement, rash, and depression. It’s essential for users to monitor their health and discuss any concerning symptoms with their healthcare provider. Understanding these potential side effects can help users make informed choices regarding their treatment.
When to Expect Hair Regrowth with Finasteride
Results from finasteride treatment can vary significantly between individuals. Generally, users may start to see initial improvements in hair density within three to six months of consistent use. Full effects may not be evident until 12 months or longer.
To achieve maximum results, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and maintain patience throughout the treatment process. Continued use, even after noticeable improvements, is necessary to sustain the benefits and counteract any future hair loss.
Comparing Finasteride with Other Hair Loss Treatments
Finasteride is often compared to minoxidil, another popular treatment for hair loss. While finasteride works by reducing DHT levels, minoxidil promotes blood flow to hair follicles and can stimulate hair growth directly. These treatments can be complementary; many users benefit from utilizing both.
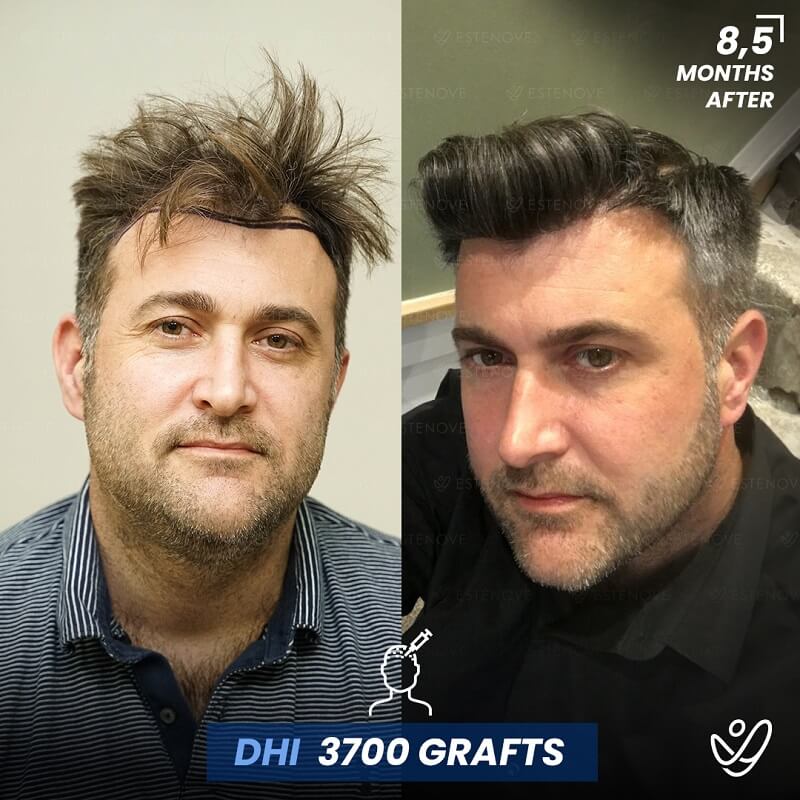
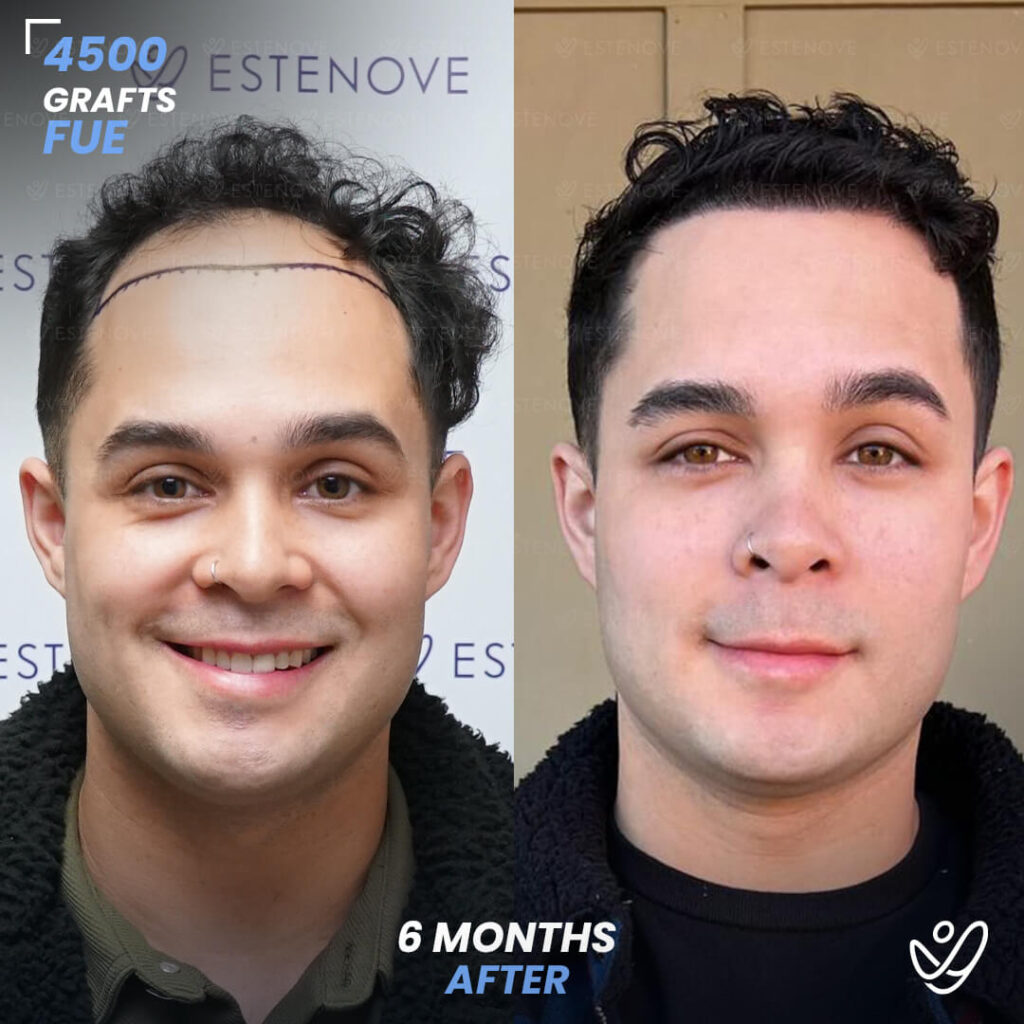
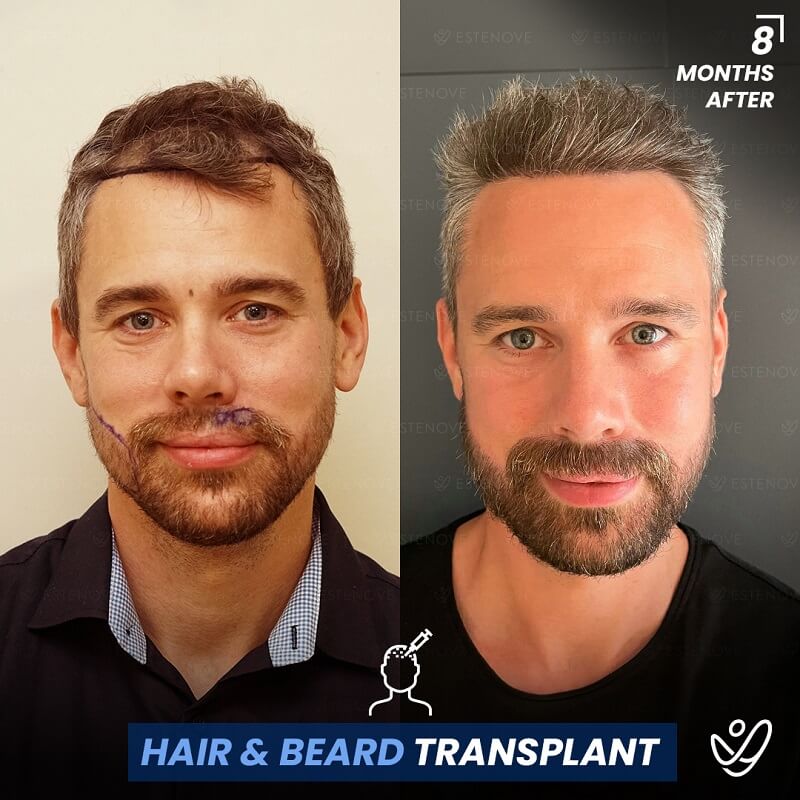
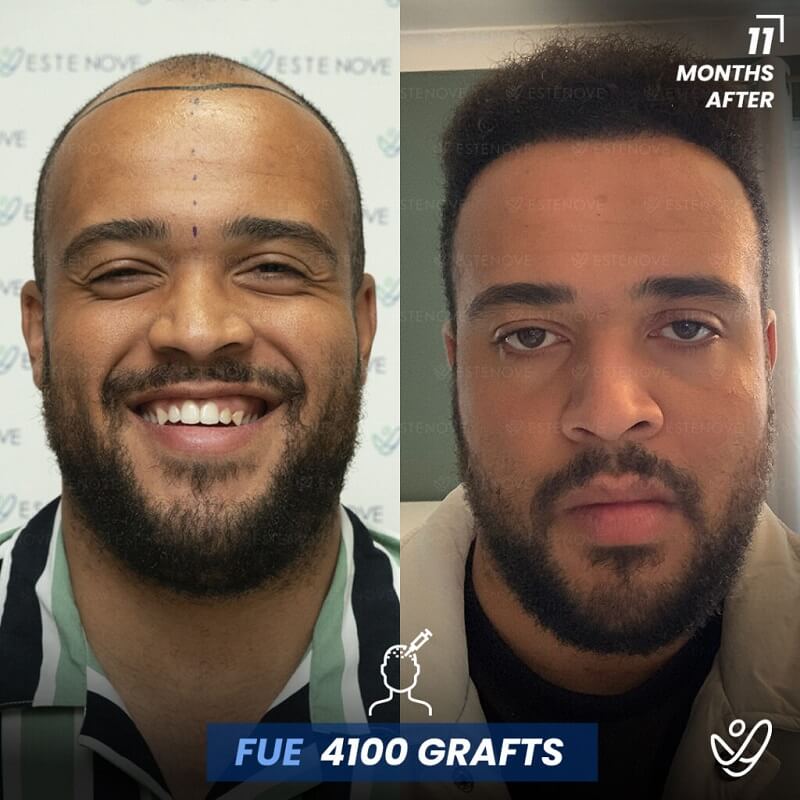
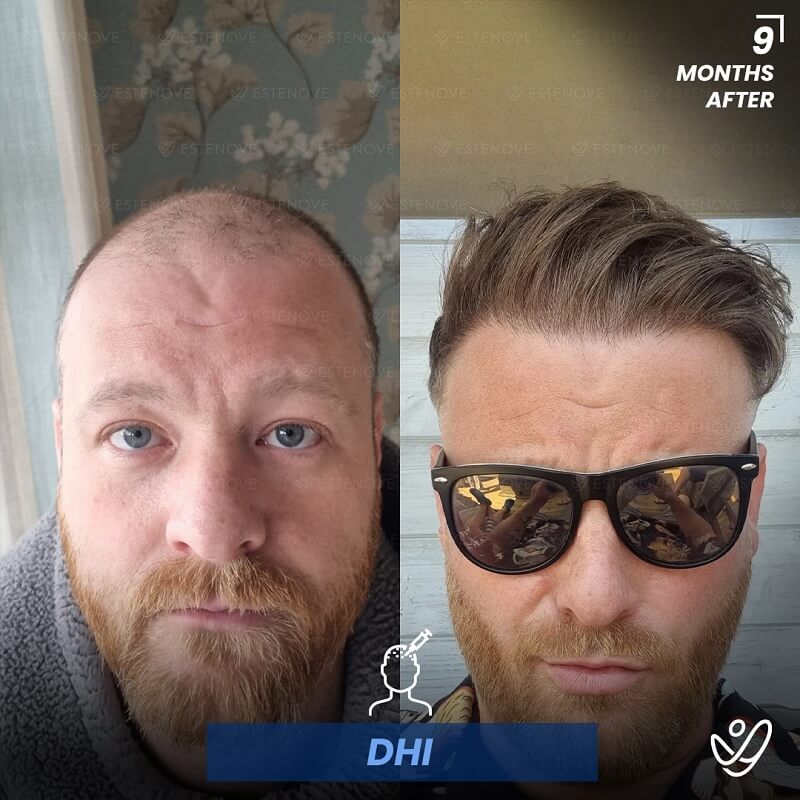
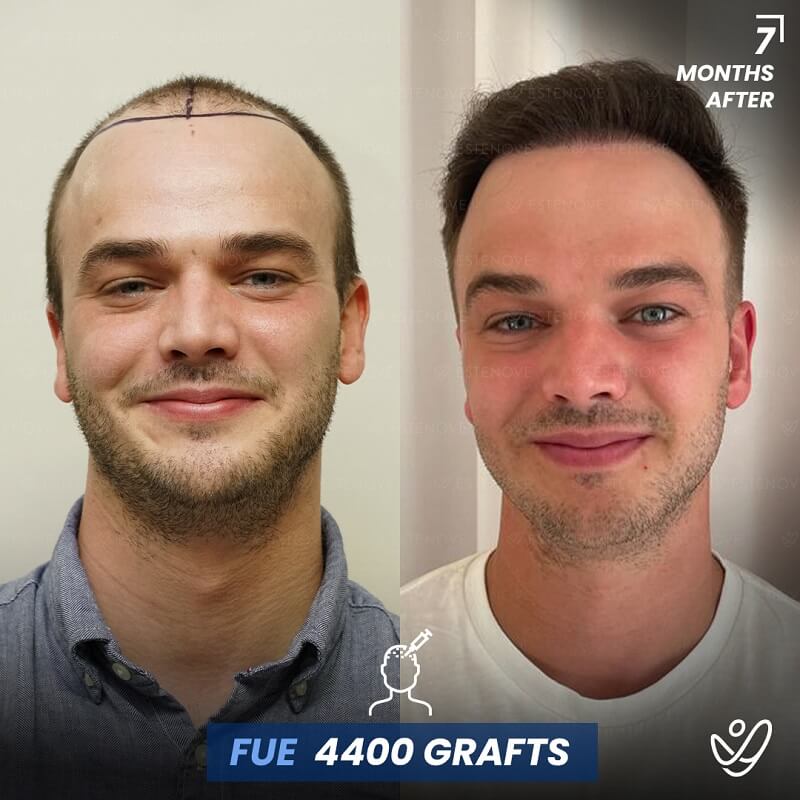
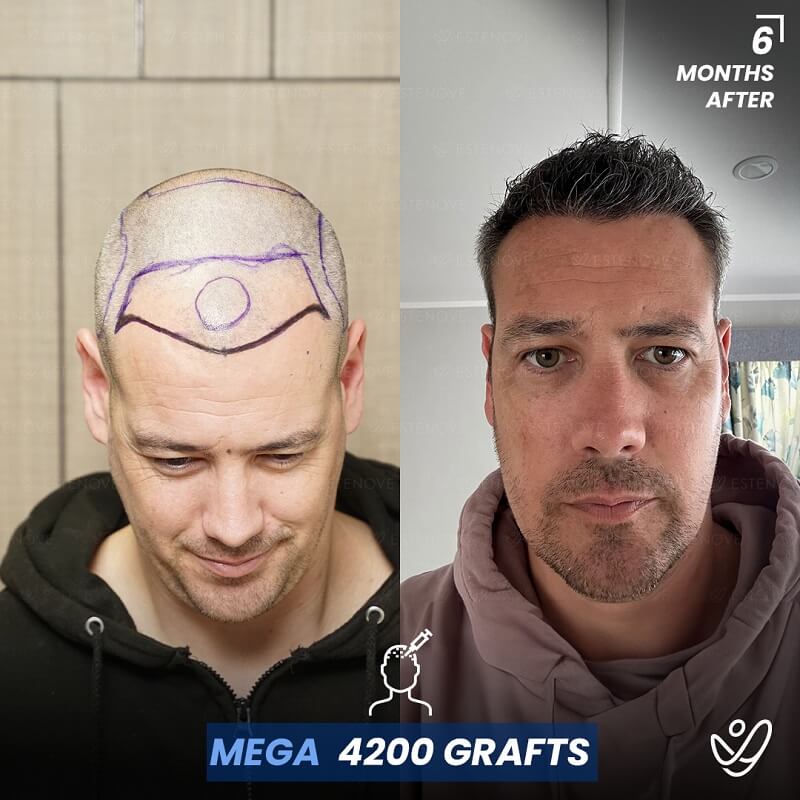
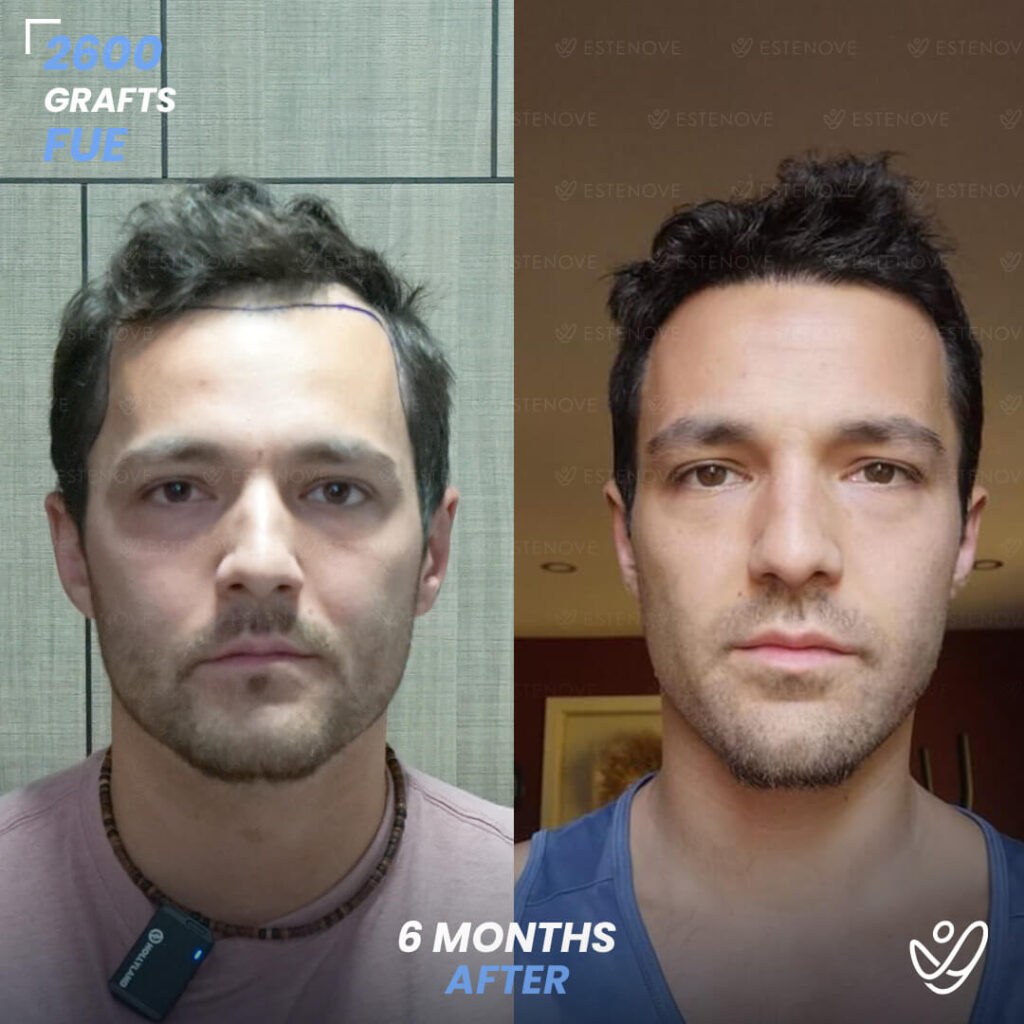
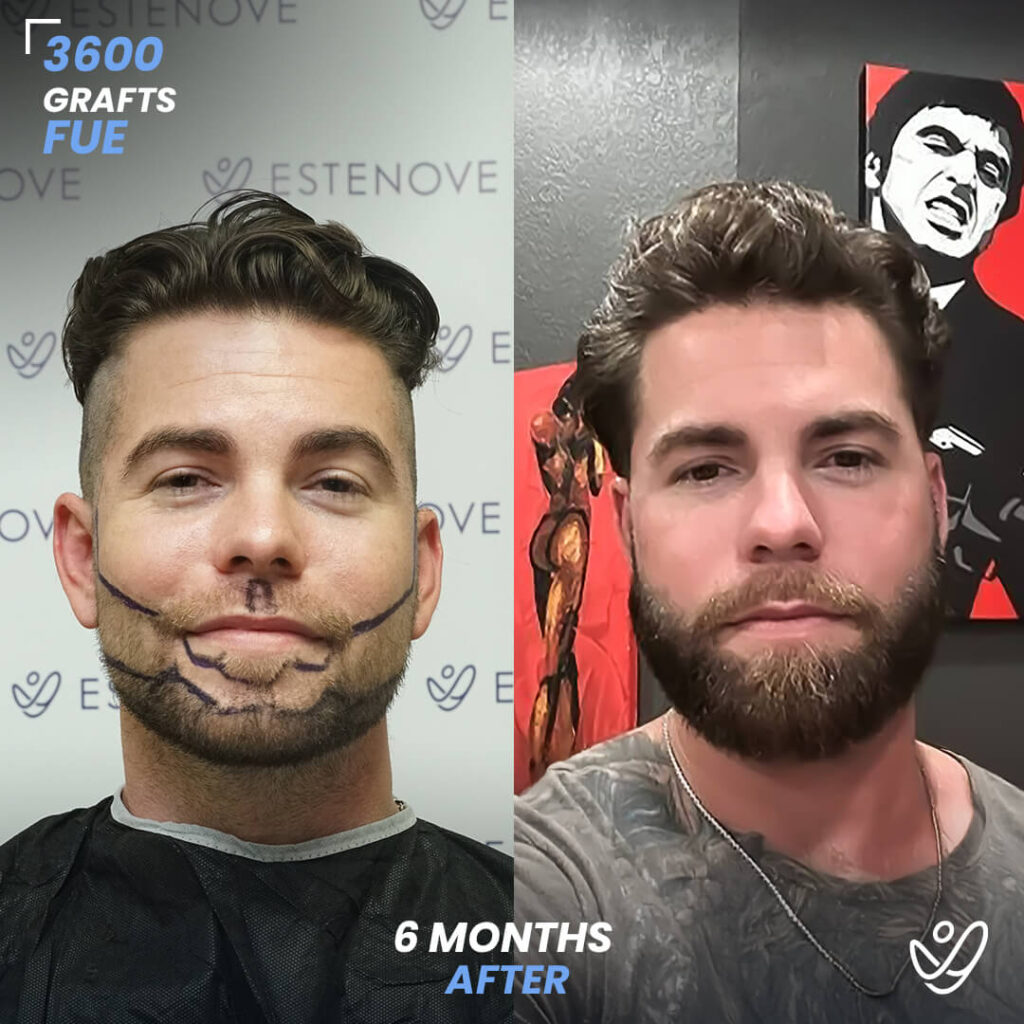
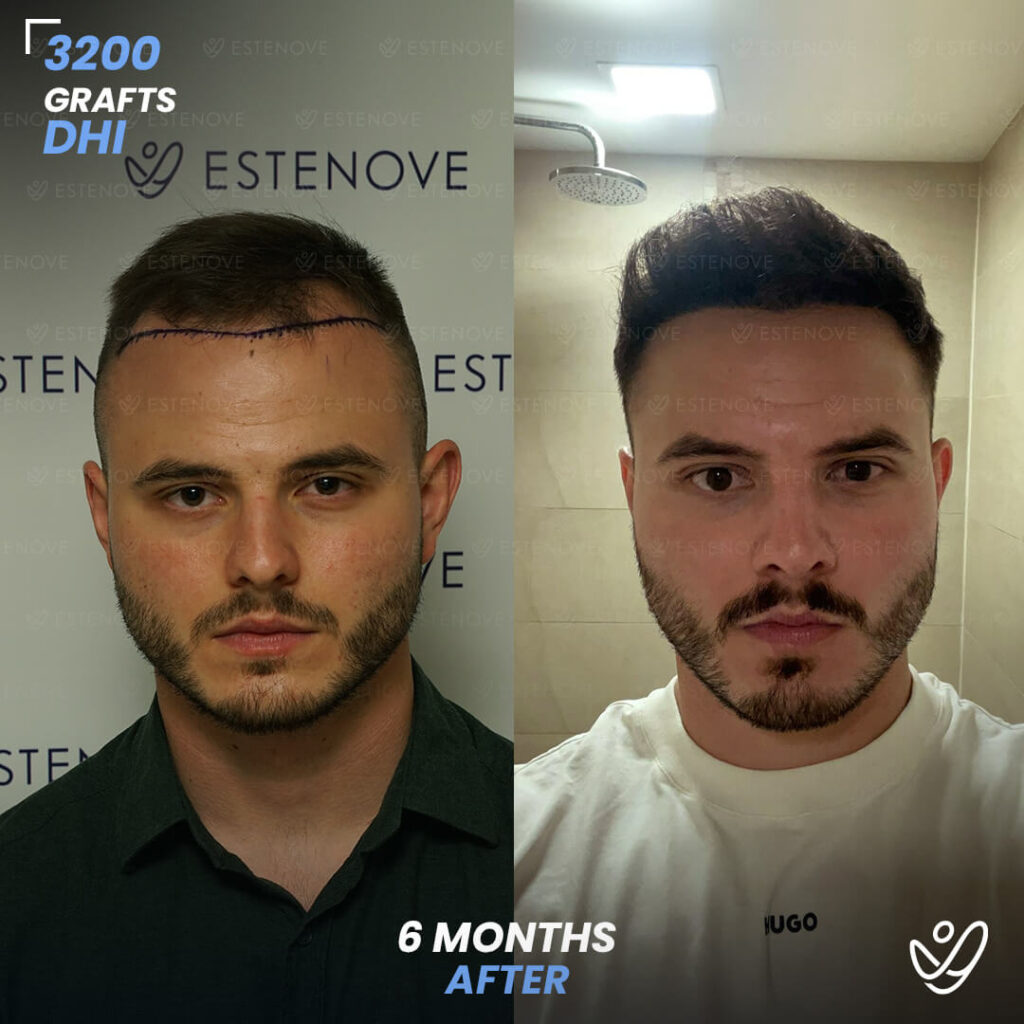
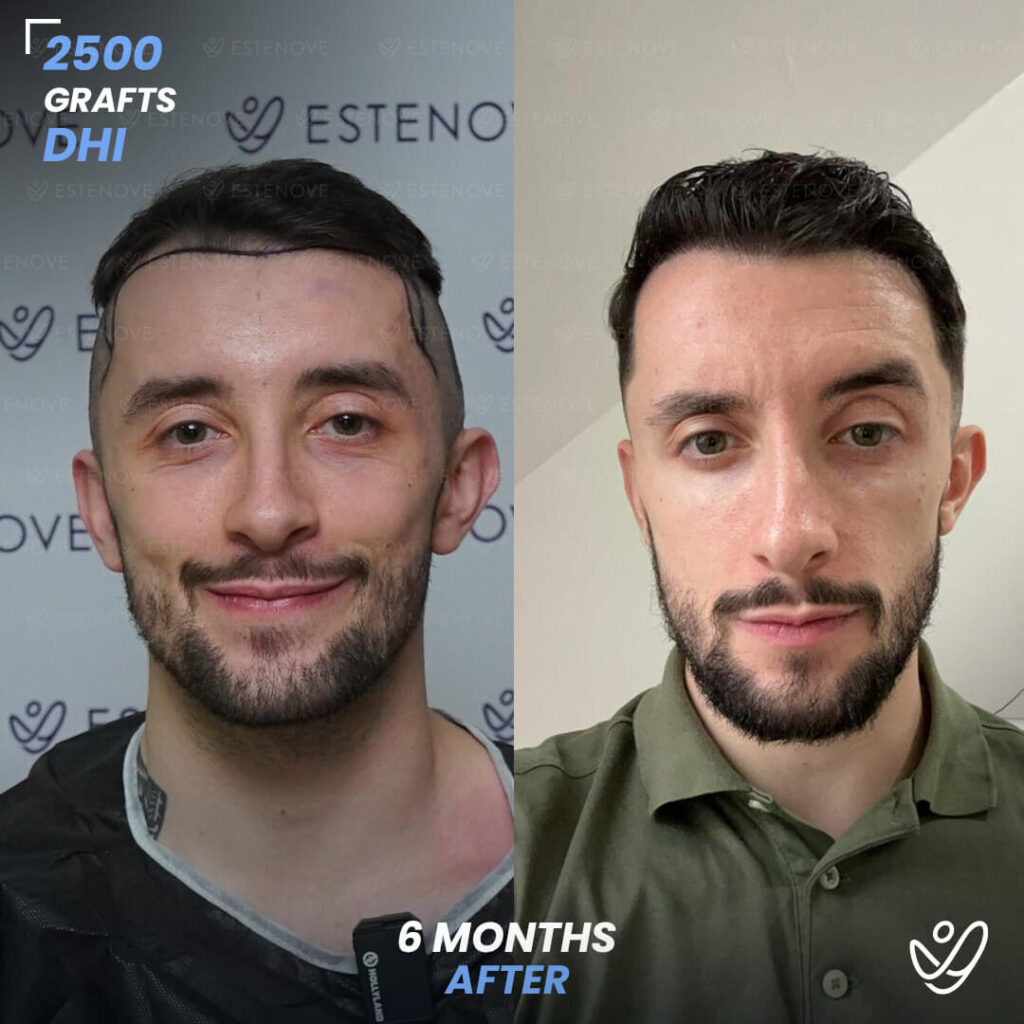
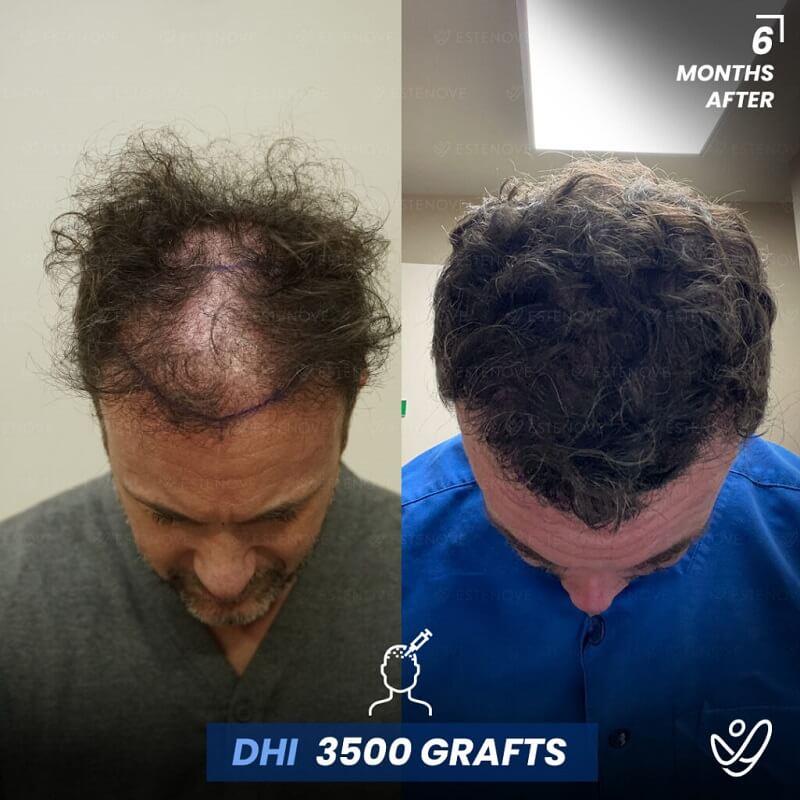
Additionally, hair transplant surgery is an alternative option for permanent hair restoration. It involves moving hair follicles from a donor site to bald or thinning areas. While effective, hair transplants are invasive and carry higher costs compared to medication. Evaluating these options can help individuals make educated decisions about their hair loss management.
Dosage and Administration: How to Use Finasteride for Hair Loss?
The standard dosage of finasteride for hair loss is 1 mg taken once a day.² It is essential to take the medication consistently to maintain stable DHT levels in the body. Finasteride can be taken with or without food, offering flexibility in administration.
Users should be advised not to exceed the recommended dosage, as higher doses do not necessarily enhance efficacy and may increase the risk of side effects. Compliance with medical guidance is paramount for safe and effective results.
Myths and Misconceptions About Finasteride
Despite its growing popularity, several myths surrounding finasteride persist. One common misconception is that finasteride is a miracle cure, which can lead to unrealistic expectations. While many users experience improvements, results can be inconsistent.
Another myth is that finasteride is only effective for older men with significant hair loss. In reality, younger men in the early stages of hair loss can also benefit from the treatment. Understanding the realities of finasteride can help individuals set appropriate expectations for their hair restoration journey.
Evaluating Options: Hair Transplant vs Medications
When faced with hair loss, individuals often consider two primary options: medical treatment or surgical intervention. Hair transplants offer a permanent solution by relocating follicles, but they require a financial investment and involve recovery time.
Conversely, medications like finasteride and minoxidil provide a less invasive approach to managing hair loss. They are typically more accessible and can be used concurrently with surgical options if desired. Individuals need to weigh the pros and cons of each method to determine the best path for their situation.
Consulting a Professional: When to Seek Medical Advice
Before starting any hair loss treatment, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. A doctor can provide personalized recommendations, evaluate underlying health conditions, and discuss potential side effects. Open dialogue about one’s goals and concerns increases the likelihood of finding effective treatment solutions.
Additionally, primary care physicians or dermatologists can offer guidance on the appropriateness of combining different treatments. Seeking professional advice is a crucial step in the journey toward successful hair restoration.
Fill the form below to get free consultation
Sources:
¹ https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/finasteride/side-effects-of-finasteride/
² https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/finasteride/how-and-when-to-take-finasteride/