What is DHT?
Dihydrotestosterone, commonly known as DHT, is an androgen hormone that is derived from testosterone. It is a vital component of the male hormonal system but also plays roles in female physiology. DHT is significantly more potent than testosterone, possessing a higher affinity for androgen receptors in the body. This means that even at lower levels, DHT can exert a powerful influence on various tissues.
The synthesis of DHT occurs through the action of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. This process can take place in various tissues, including the skin, hair follicles, and prostate gland. Understanding the basics of DHT is crucial, especially due to its significant impacts on health, hair growth, and development.
DHT plays a crucial role in the development of male characteristics during puberty, such as facial hair growth, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass. In addition to these physical changes, DHT is also involved in the regulation of libido and sexual function. However, its effects are not limited to males; in females, DHT contributes to the maintenance of healthy skin and hair, although imbalances can lead to conditions such as hirsutism or acne. The dual role of DHT in both male and female physiology highlights its importance in understanding hormonal health across genders.
Moreover, the levels of DHT in the body can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, age, and overall health. For instance, as men age, the activity of 5-alpha reductase can increase, leading to higher levels of DHT, which may contribute to conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness. In women, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can result in elevated DHT levels, leading to hair thinning and other hormonal imbalances. This complexity underscores the need for a nuanced understanding of DHT’s role in both health and disease, making it a critical area of study in endocrinology and dermatology.
The Role of DHT in the Human Body
DHT is involved in several important functions within the human body. In males, it contributes to the development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics during puberty, such as the growth of facial hair, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass. Additionally, DHT plays a role in the sexual functioning of males, influencing libido and erectile function.
In females, DHT is present at lower levels and is involved in hormonal balance. It also contributes to the health of the skin and hair follicles. Beyond sexual characteristics, DHT affects several metabolic processes, showcasing its influence throughout the body. However, while DHT has many beneficial roles, an overproduction or heightened sensitivity to this hormone can lead to multiple health concerns, particularly regarding hair loss.
How DHT Affects Hair Growth and Loss
The connection between DHT and hair follicles has been extensively studied, particularly in the context of androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male and female pattern baldness. DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, triggering a phase of hair growth known as anagen. However, this binding also causes follicle miniaturization over time, resulting in thinner and shorter hair strands.
As hair follicles become increasingly sensitive to DHT, they enter a shortened growth phase, leading to hair loss. This process can lead to noticeable thinning of hair and, in severe cases, complete baldness in certain areas. Understanding how DHT interacts with hair follicles is crucial for developing effective treatments for hair loss and understanding the underlying mechanisms involved.
DHT and Male vs. Female Hair Loss
While DHT plays a central role in hair loss for both genders, the patterns and implications differ between males and females. In males, androgenetic alopecia often presents as a receding hairline or thinning on the crown. This hair loss is usually progressive and correlates directly with DHT levels.
In contrast, females experience a more diffuse thinning of hair across the scalp. While female pattern baldness is also associated with DHT, the hormonal landscape in women is more complex due to the influence of estrogen and other hormones. This difference highlights the need for personalized approaches to diagnosis and treatment for hair loss in each gender.
Treatments Targeting DHT
Given the impact of DHT on hair loss, various treatment options have been developed to mitigate its effects. One of the most popular treatments is finasteride, a prescription medication that inhibits the activity of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, thereby reducing DHT levels in the scalp and promoting healthier hair growth.
Alternatives to medication include topical treatments like minoxidil, which promote blood flow to hair follicles and can help reverse some of the effects of DHT. Other natural approaches involve the use of saw palmetto, which is thought to have similar DHT-blocking properties, although research on its efficacy is ongoing.
It is essential for individuals considering these treatments to consult a healthcare professional to develop a tailored approach that suits their specific needs and health status.
FAQs About DHT and Hair Loss
As DHT remains a topic of significant interest, many individuals have questions regarding its role in hair loss. Below are some frequently asked questions:
- Can I lower my DHT levels naturally? Yes, certain lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and herbal supplements may help manage DHT levels.
- Is hair loss due to DHT reversible? In many cases, yes. Early intervention using treatments targeting DHT may promote hair regrowth.
- Are there side effects to DHT-blocking medications? Some individuals may experience side effects, including changes in libido or mood. It’s best to consult a healthcare provider.
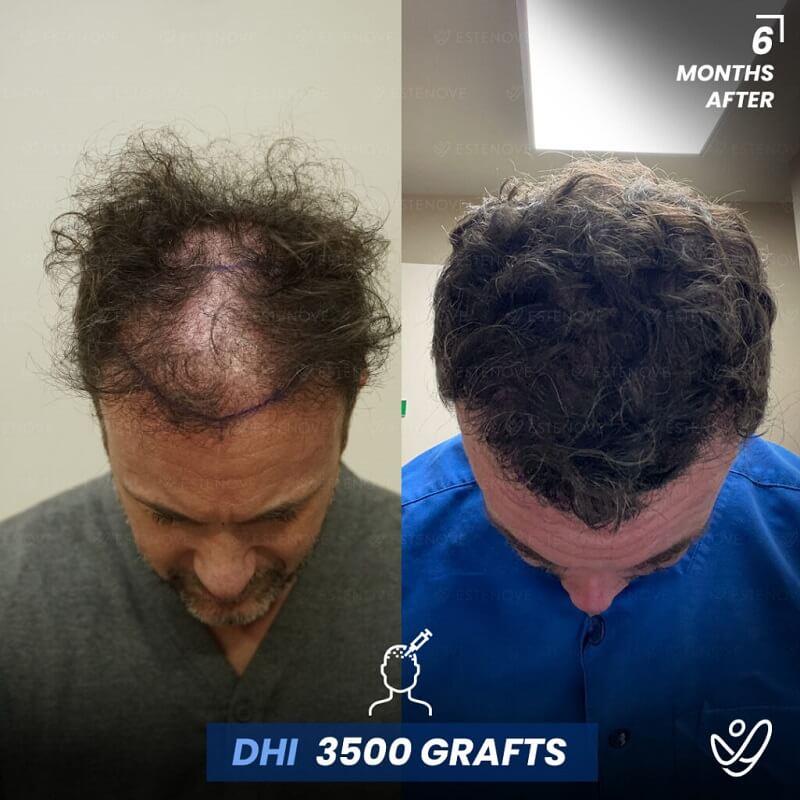
Hair Transplants as a Solution
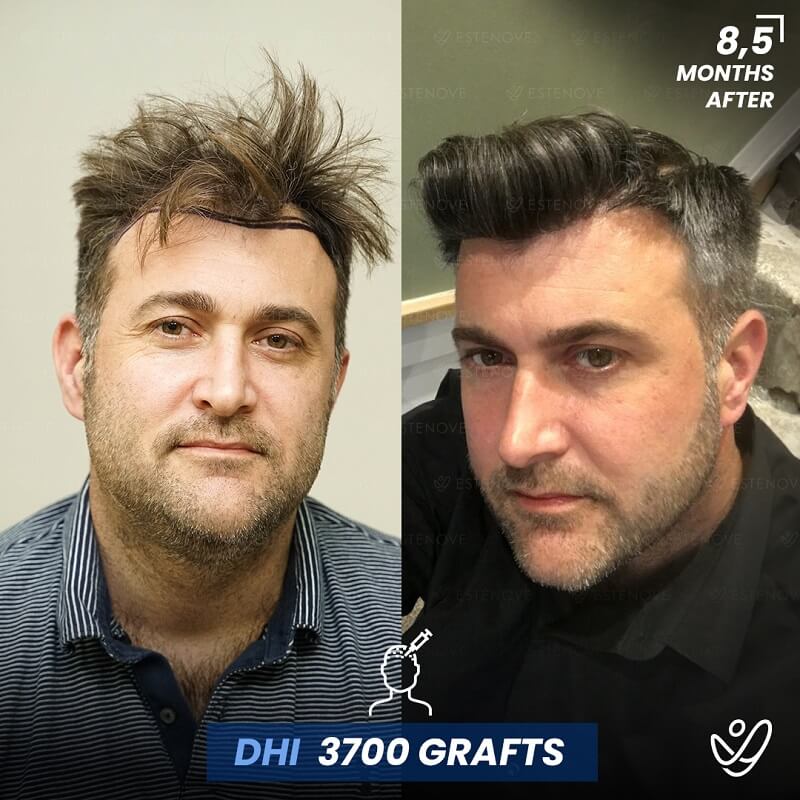
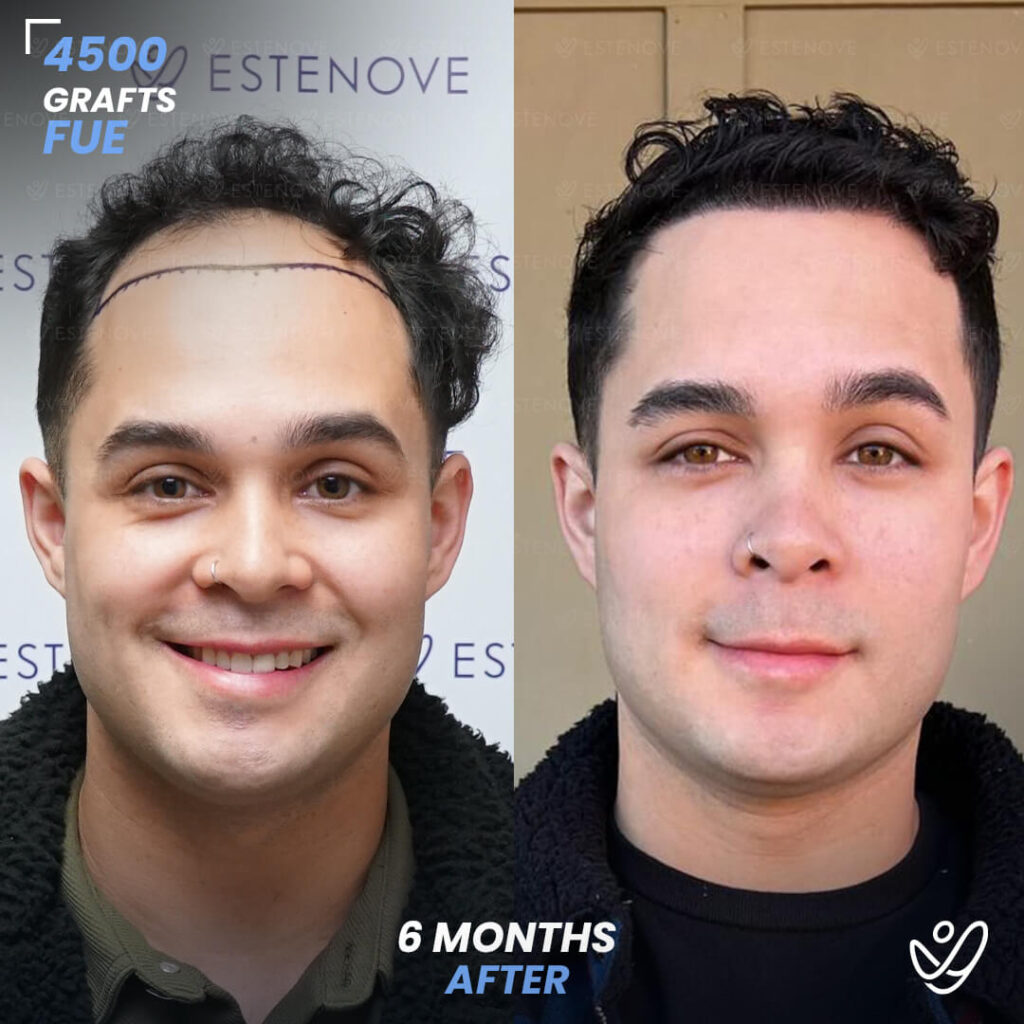
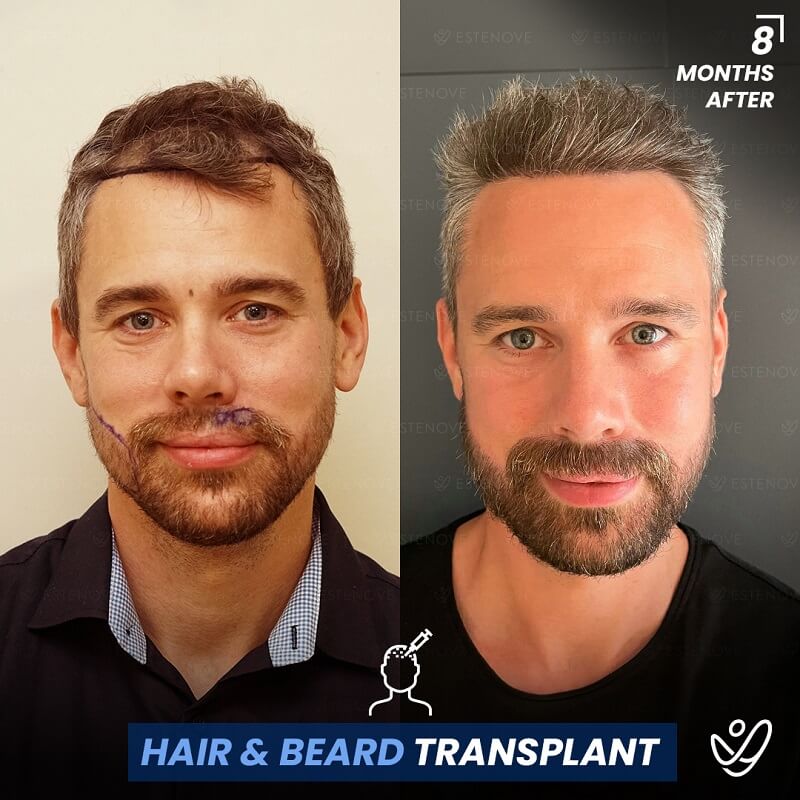
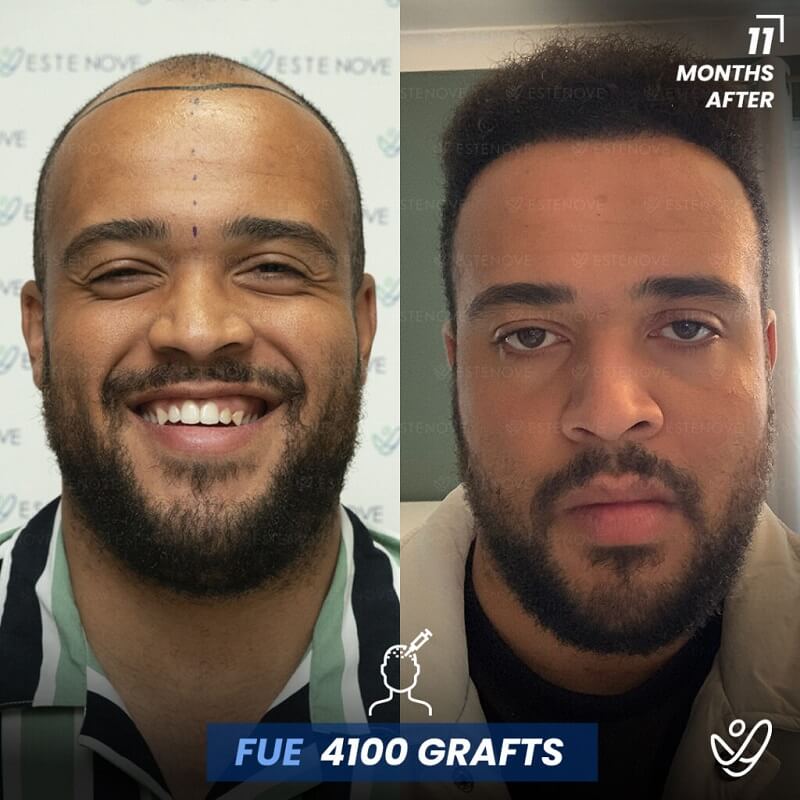
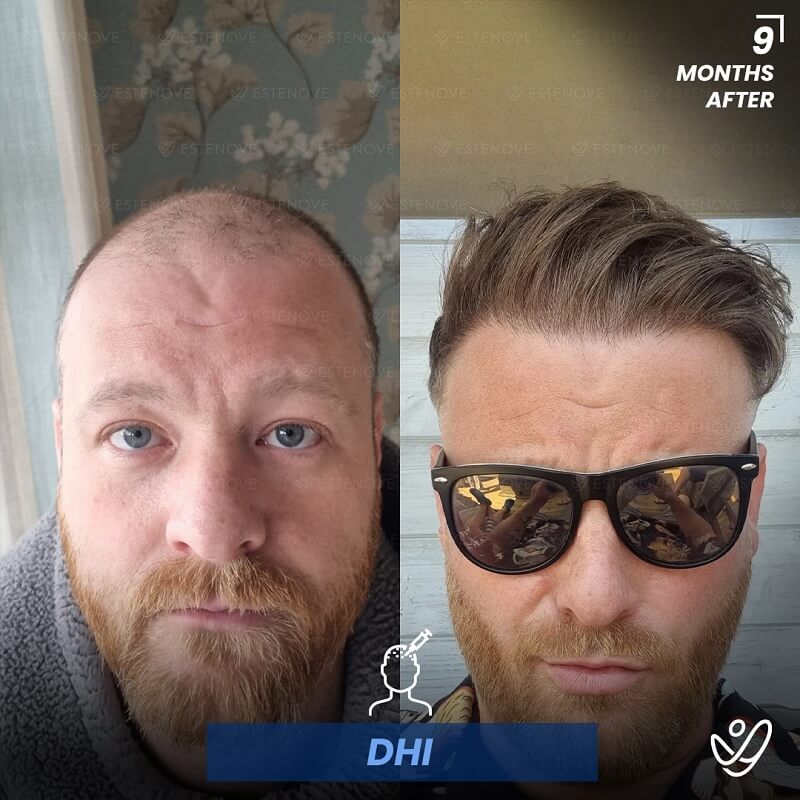
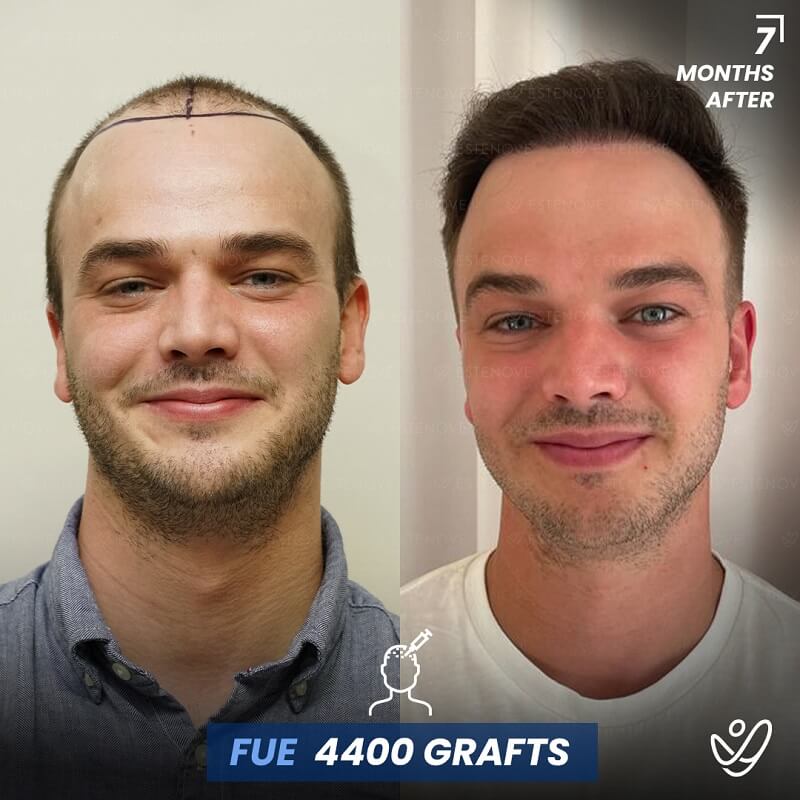
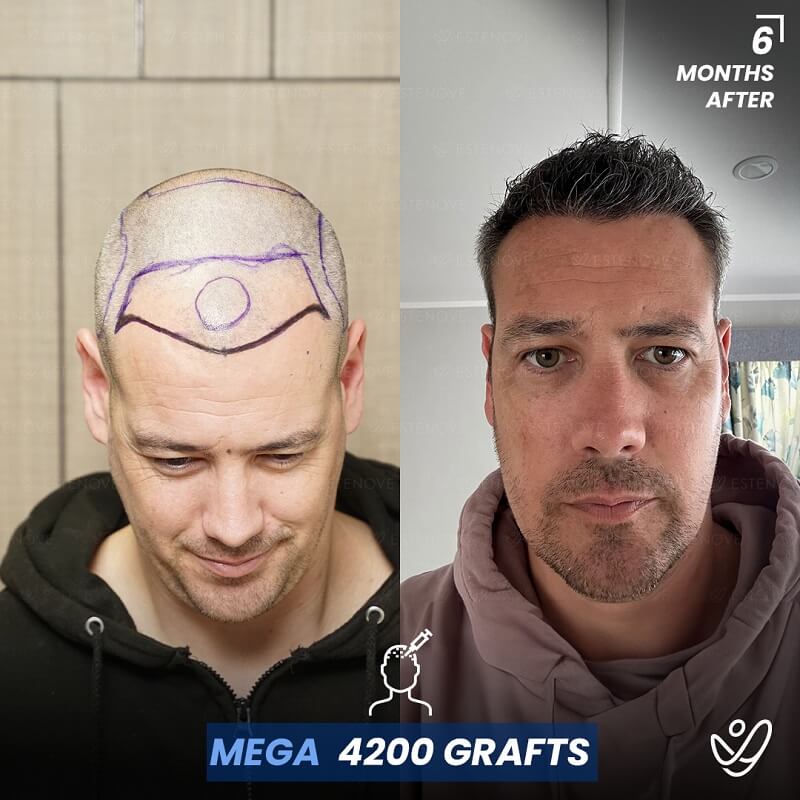
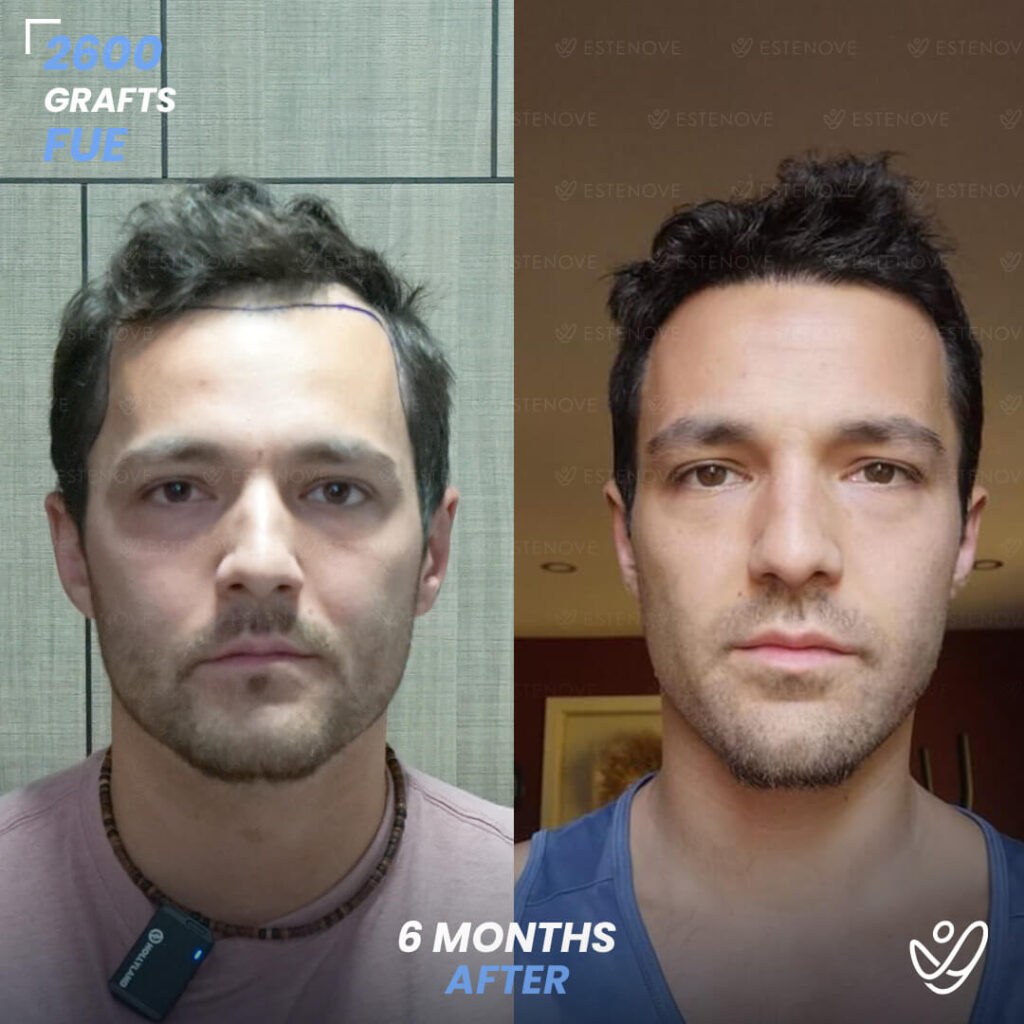
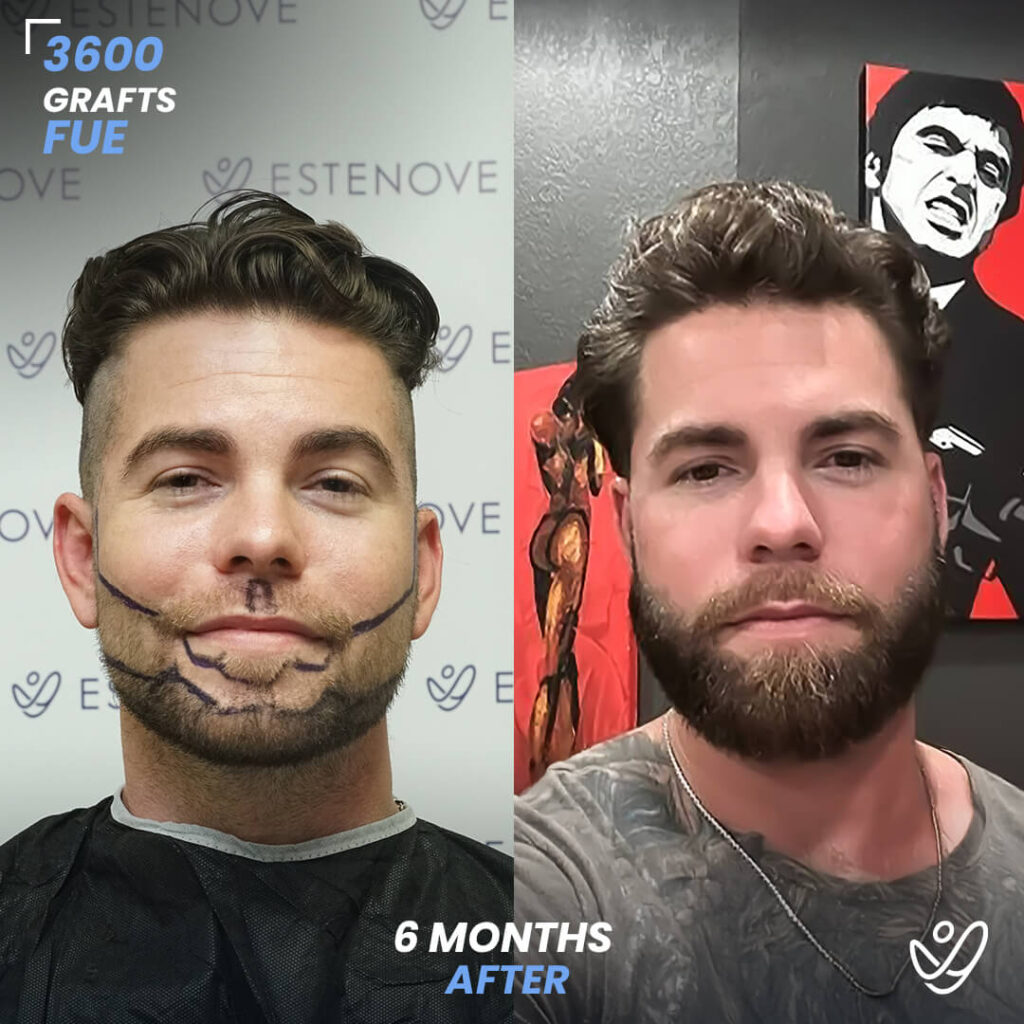
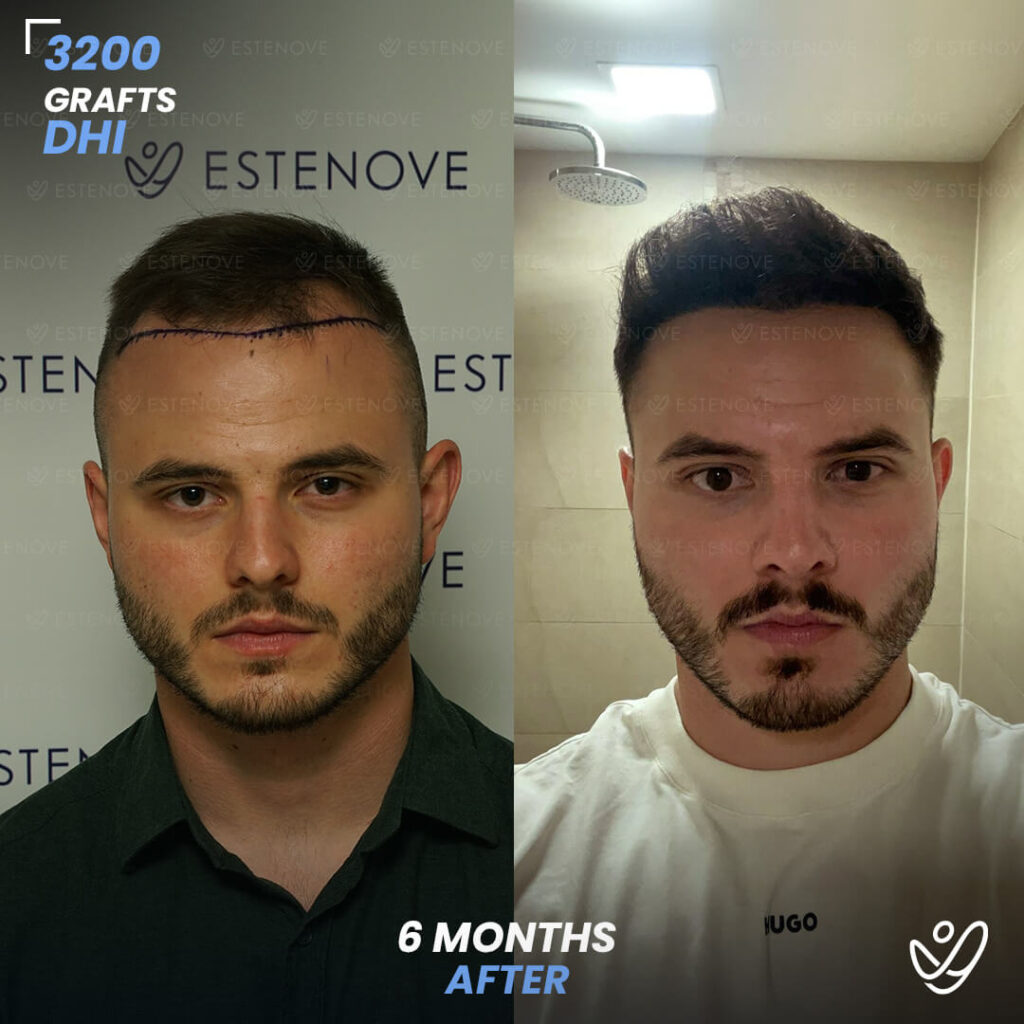
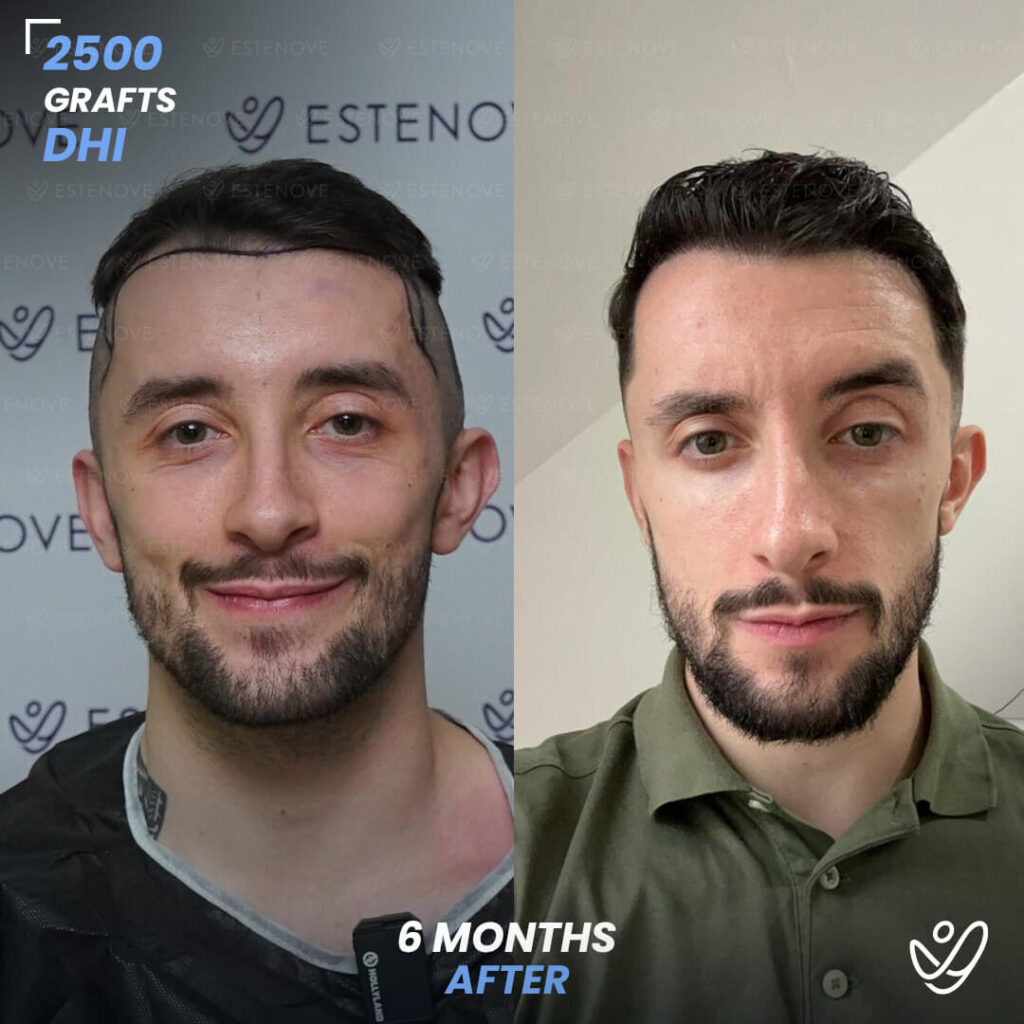
For those who experience significant hair loss due to DHT, hair transplant surgery can offer a more permanent solution. This procedure involves the extraction of hair follicles from donor sites and their implantation into balding areas of the scalp. It provides a way to restore a natural appearance and mitigate the effects of DHT on hair follicles.
Hair transplants have a high success rate¹ and can yield impressive results for individuals who are good candidates for the procedure. As with any surgical intervention, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and consult with a qualified hair restoration specialist to evaluate options and expected outcomes.
In summary, DHT is a critical hormone with significant implications for hair growth and loss. Understanding its role can pave the way for targeted treatments and informed health decisions regarding hair loss management.
Fill the form below to get free consultation
Sources:
¹ Beehner, M. L. (1999). A comparison of hair growth between follicular-unit grafts trimmed “skinny” vs.“chubby”. Dermatologic surgery, 25(4), 339-340.