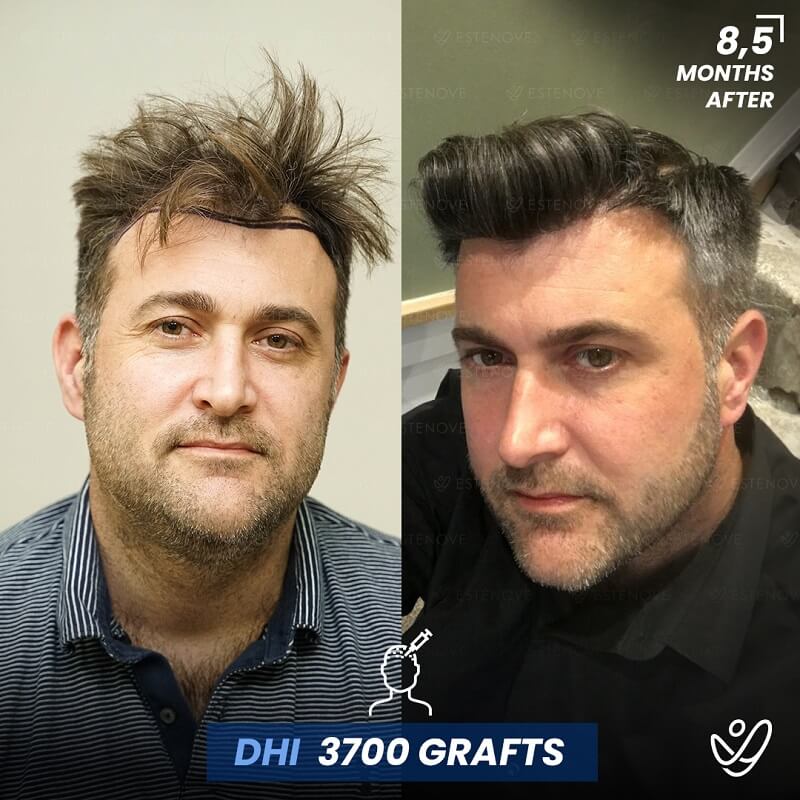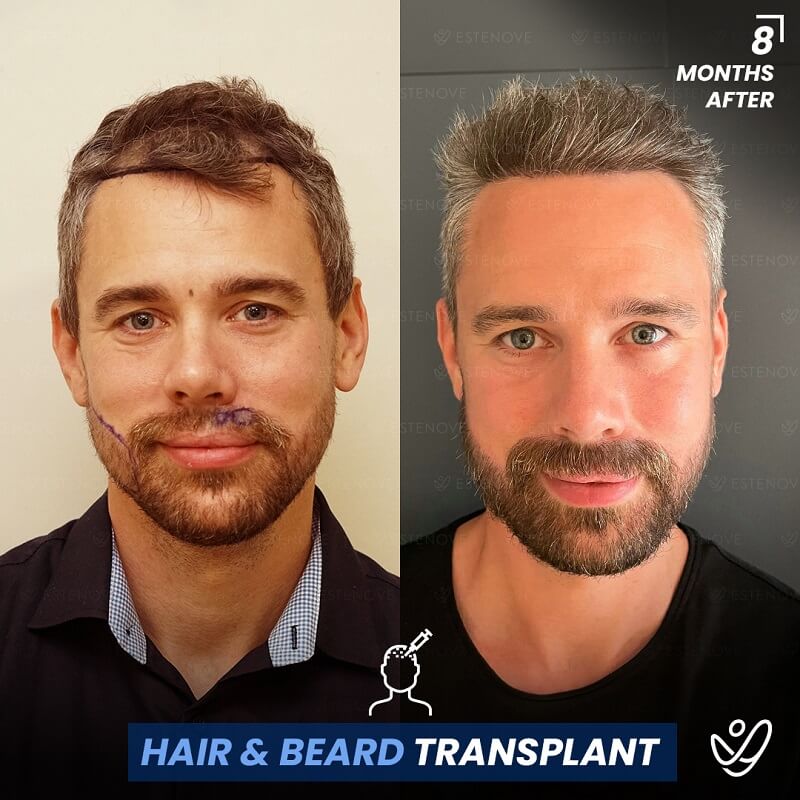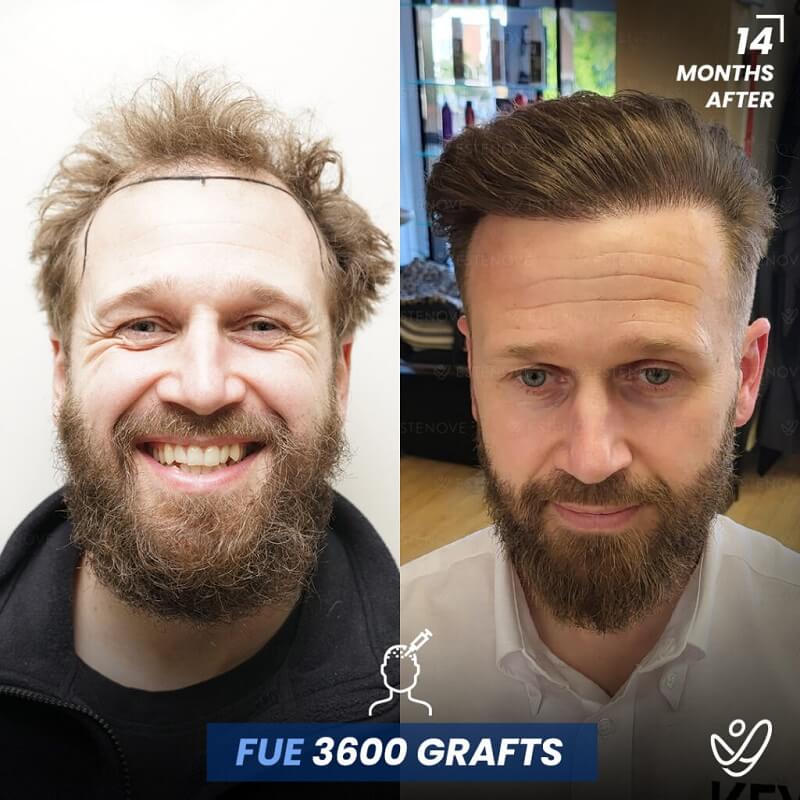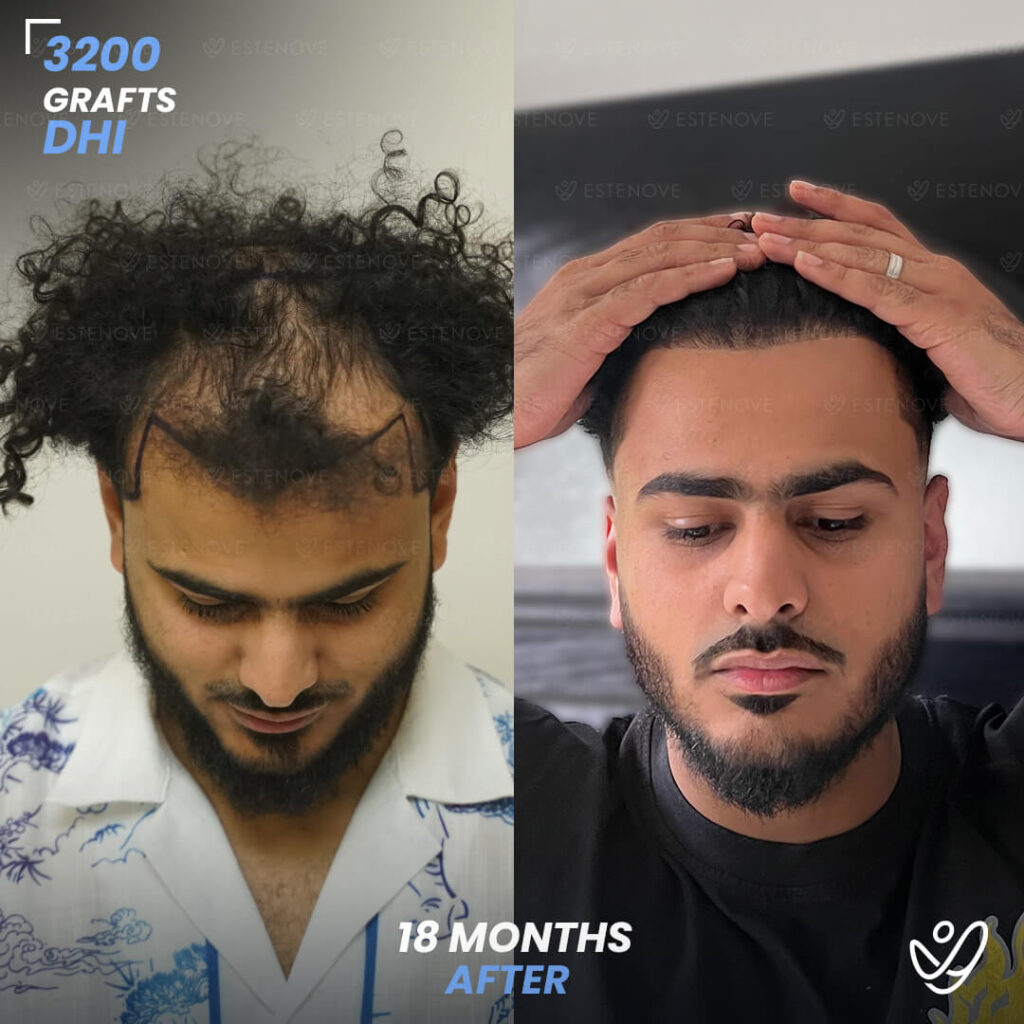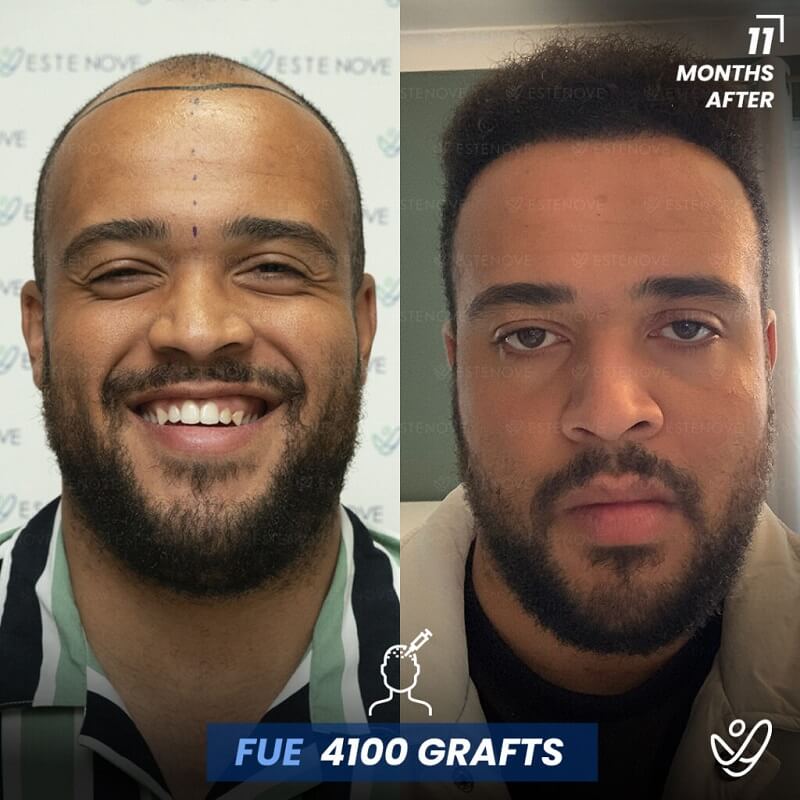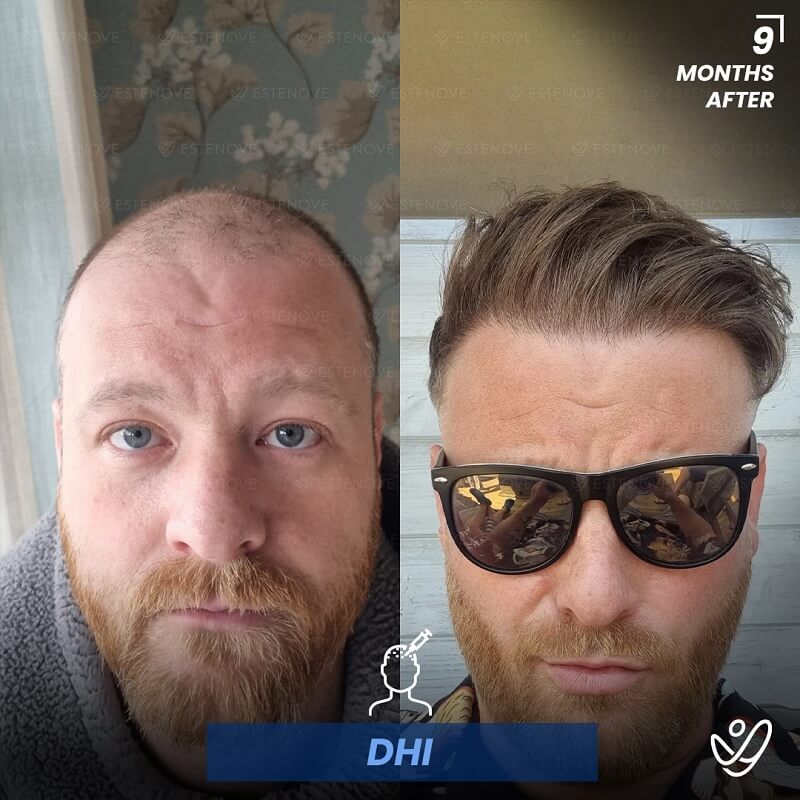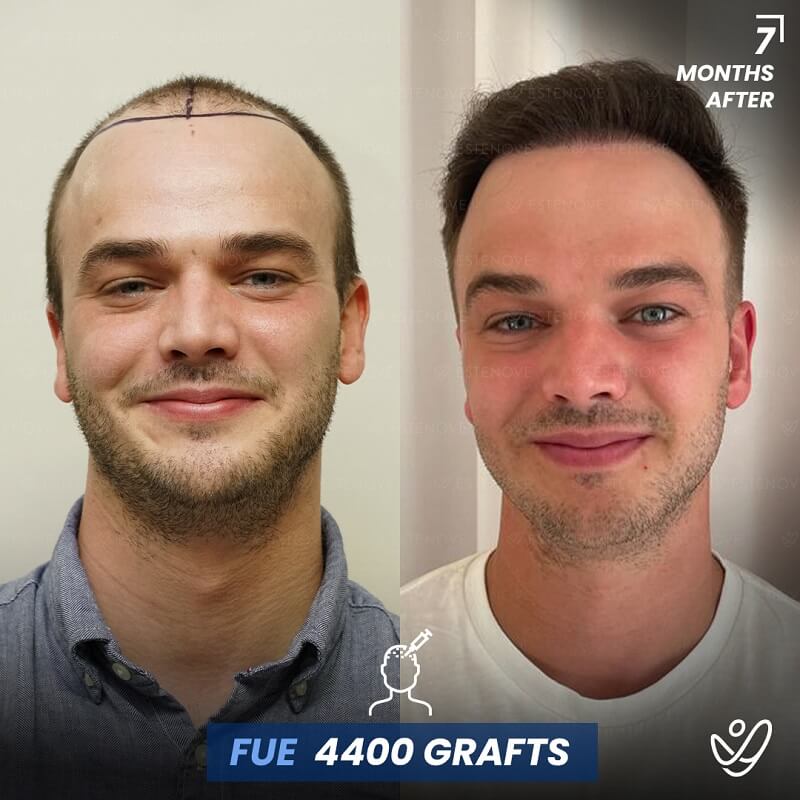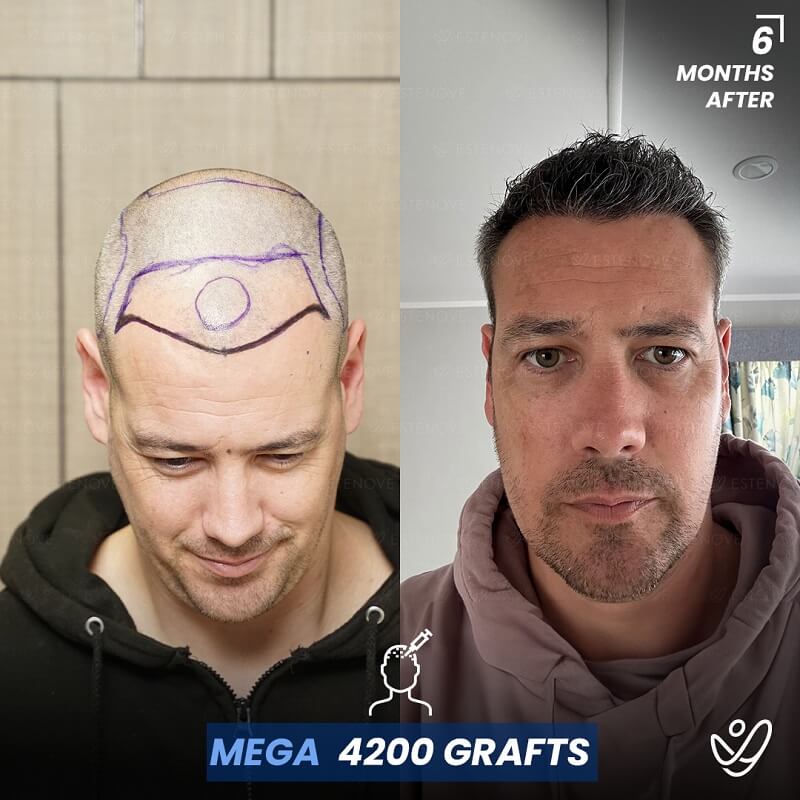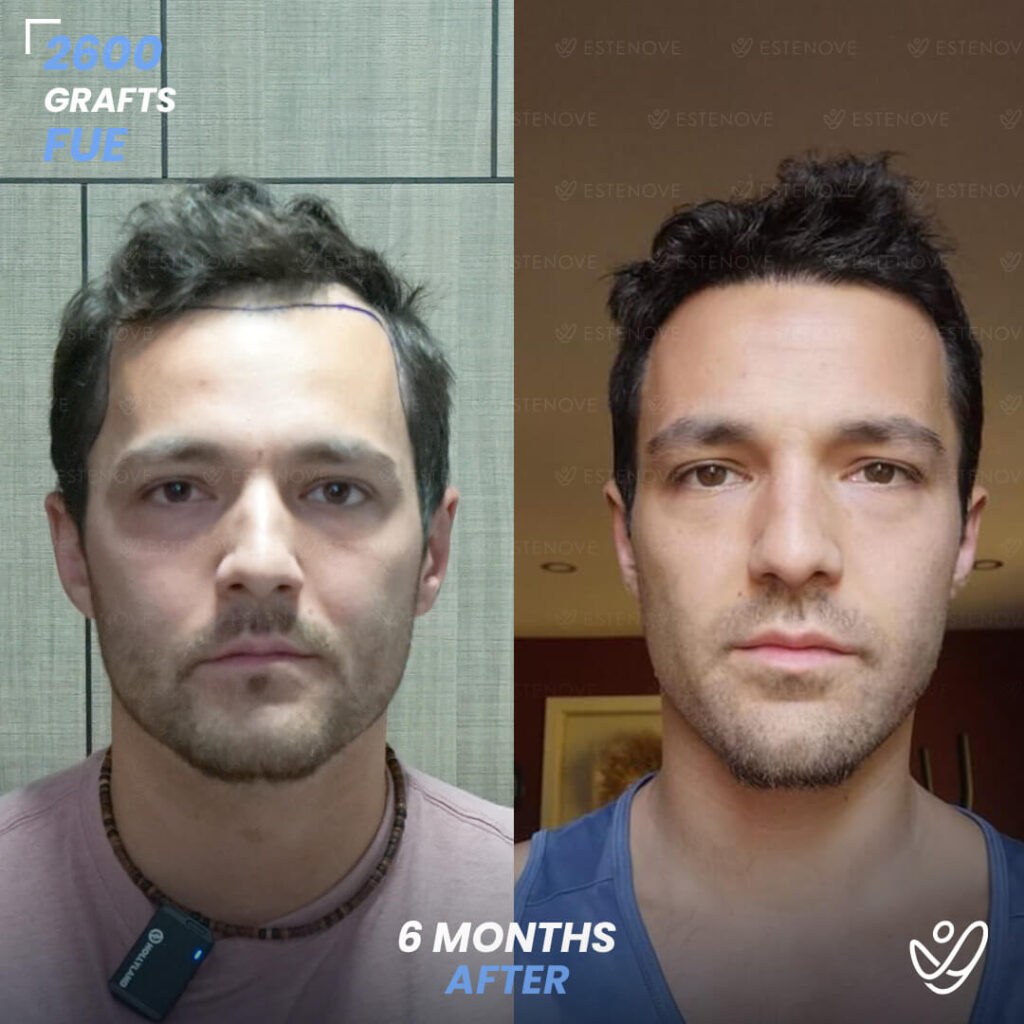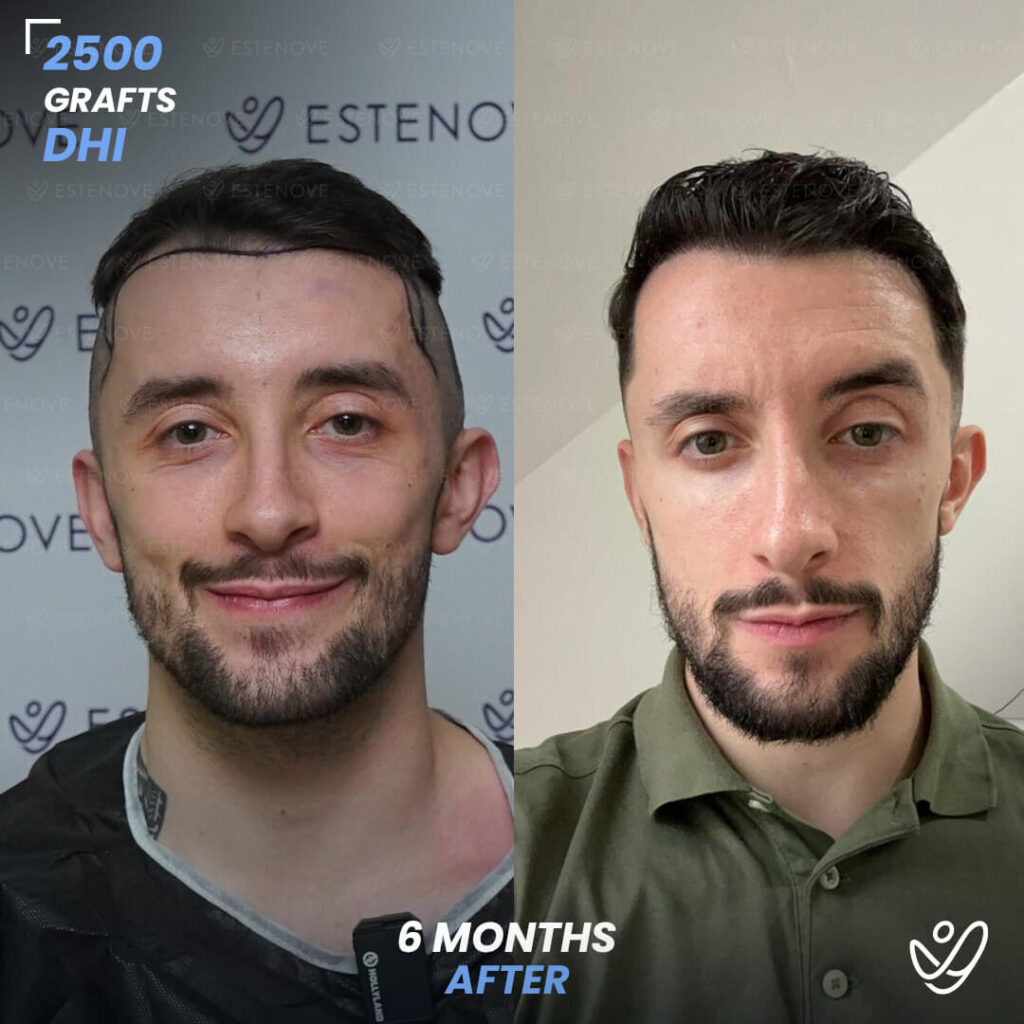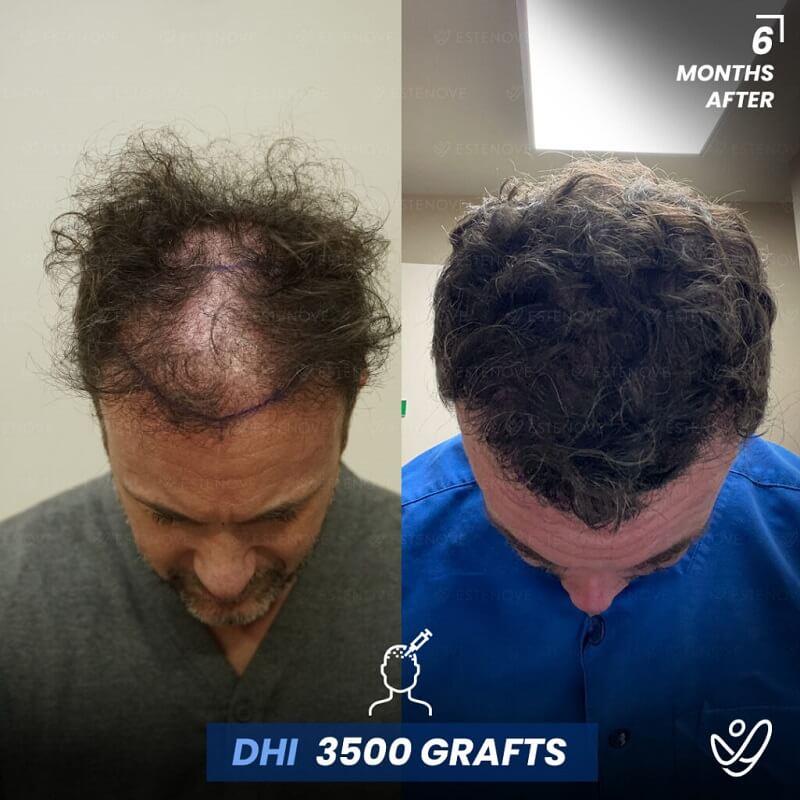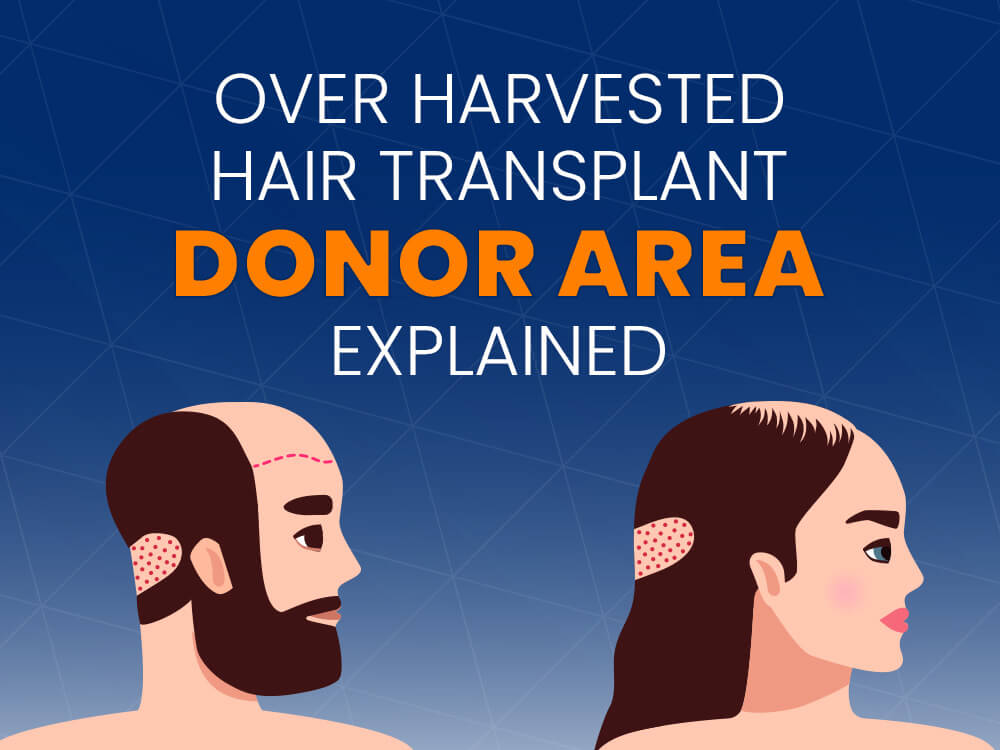
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body, known as the ‘donor site’, to a bald or balding part of the body, known as the ‘recipient site’. The process is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness, although it can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, and to fill in scars caused by accidents or surgery. One of the key aspects of a successful hair transplant is the careful management of the donor area. Over-harvesting of the donor area is a common issue that can lead to a number of complications.
In this glossary entry, we will delve into the concept of an over-harvested donor area in the context of hair transplantation. We will explore what this term means, why it happens, the potential consequences, and how it can be prevented or managed. This is a critical topic for anyone considering a hair transplant, as well as for medical professionals in the field.
Understanding the Donor Area
The donor area is the part of the body from which hair follicles are taken during a hair transplant. This is typically the back of the head, as this area is genetically resistant to the effects of DHT, a hormone that causes hair loss. The hair in this area is more likely to remain healthy and grow even when transplanted to a different part of the body.
However, the donor area is not an unlimited resource. There is a finite number of hair follicles in this area, and once they are removed, they cannot be replaced. This is why it is crucial to manage the donor area carefully during a hair transplant procedure, to ensure that there are enough hair follicles left for future needs, and to avoid causing unnecessary damage or scarring.
What is Over-Harvesting?
Over-harvesting refers to the removal of too many hair follicles from the donor area during a hair transplant. This can occur if the surgeon is not careful, or if the patient’s hair loss is more severe than anticipated. Over-harvesting can lead to a number of problems, including a thin or patchy appearance in the donor area, scarring, and a reduced ability to perform future hair transplants.
It’s important to note that over-harvesting is not always immediately apparent. It may only become noticeable once the hair in the donor area has had a chance to regrow, which can take several months. This is why it is crucial to choose a reputable and experienced hair transplant clinic, such as Estenove, to ensure that the procedure is carried out correctly and the donor area is managed effectively.
Consequences of Over-Harvesting
Over-harvesting of the donor area can have a number of negative consequences. Firstly, it can lead to a thin or patchy appearance in the donor area. This can be particularly noticeable if the patient has short hair, or if the hair is wet. In some cases, the skin in the donor area may also become visible, which can be distressing for the patient.
Secondly, over-harvesting can lead to scarring in the donor area. This can occur if too many hair follicles are removed at once, or if the extraction process is not carried out correctly. Scarring can be both a cosmetic and a medical issue, as it can affect the appearance of the donor area and potentially cause discomfort or pain.
Impact on Future Hair Transplants
Perhaps the most significant consequence of over-harvesting is its impact on future hair transplants. If too many hair follicles are removed from the donor area, it may not be possible to perform additional hair transplants in the future. This can be a major issue for patients who experience continued hair loss after their initial transplant, as they may not have enough donor hair left to address their ongoing needs.
Furthermore, if the donor area is scarred or damaged due to over-harvesting, this can make future hair transplants more difficult and potentially less successful. This is why it is so important to manage the donor area carefully during a hair transplant, to ensure that there are enough healthy hair follicles left for future needs.
Preventing Over-Harvesting
There are several strategies that can be used to prevent over-harvesting of the donor area during a hair transplant. The first is careful planning and assessment. Before the procedure, the surgeon should assess the patient’s hair loss and the condition of their donor area, to determine how many hair follicles can be safely removed. This should be done in consultation with the patient, taking into account their goals and expectations for the procedure.
Another key strategy is the use of appropriate extraction techniques. There are two main methods used to extract hair follicles during a hair transplant: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Both methods have their pros and cons, and the choice between them should be based on the patient’s individual needs and the condition of their donor area.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as strip harvesting, involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, from which the hair follicles are then extracted. This method can allow for a large number of hair follicles to be transplanted at once, but it can also lead to scarring in the donor area. However, with careful surgical technique and post-operative care, this scarring can be minimized.
One of the advantages of FUT is that it allows for the efficient transplantation of a large number of hair follicles. This can be particularly beneficial for patients with severe hair loss, who may require a large number of grafts to achieve their desired results. However, because FUT involves the removal of a strip of skin, it can also lead to a linear scar in the donor area. This scar can usually be hidden by the patient’s remaining hair, but it may be visible if the hair is cut very short.
Calculate the number of grafts needed for your hair transplant and get an estimated cost for various destinations: Try graft calculator
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE, on the other hand, involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area, without the need to remove a strip of skin. This method can reduce the risk of scarring, but it can also be more time-consuming and potentially more expensive than FUT. However, FUE can be a good option for patients with a limited donor area, as it allows for a more selective extraction of hair follicles.
One of the main advantages of FUE is that it can reduce the risk of scarring in the donor area. Because individual hair follicles are extracted, rather than a strip of skin, there is no linear scar left behind. However, FUE can still cause small, dot-like scars in the donor area, although these are usually less noticeable than the scar from FUT. FUE can also be more time-consuming than FUT, as each hair follicle must be extracted individually. However, with the use of modern, automated FUE devices, this process can be significantly sped up.
Managing an Over-Harvested Donor Area
If over-harvesting of the donor area has already occurred, there are several strategies that can be used to manage the situation. The first step is to assess the extent of the over-harvesting and the condition of the donor area. This can be done through a physical examination and possibly imaging studies, such as a trichoscopy or a dermatoscopy.
Once the extent of the over-harvesting has been determined, the next step is to develop a treatment plan. This may involve medical treatments to promote hair growth in the donor area, surgical treatments to repair any scarring, or a combination of both. The specific treatments used will depend on the patient’s individual needs and the condition of their donor area.
Medical Treatments
There are several medical treatments that can be used to promote hair growth in an over-harvested donor area. These include topical treatments, such as minoxidil, and oral medications, such as finasteride. These treatments work by stimulating the hair follicles to grow, which can help to improve the appearance of the donor area.
However, it’s important to note that these treatments are not a cure for over-harvesting. They can help to improve the appearance of the donor area, but they cannot replace the lost hair follicles. Therefore, these treatments should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, rather than as a standalone solution.
Surgical Treatments
In some cases, surgical treatments may be needed to repair an over-harvested donor area. This can involve a number of different procedures, depending on the extent of the over-harvesting and the condition of the donor area.
One option is to perform a second hair transplant, using hair follicles from a different donor area. This can be a good option for patients who have sufficient hair in other areas of their body, such as the beard or chest. However, this option is not suitable for all patients, and the results can vary depending on the quality of the donor hair.
Another option is to use scalp micropigmentation or hair tattooing to create the illusion of a fuller head of hair. This involves applying small dots of pigment to the scalp, to mimic the appearance of hair follicles. This can be a good option for patients who are not candidates for a second hair transplant, or who want to improve the appearance of their donor area without undergoing further surgery.
Choosing the Right Hair Transplant Clinic
One of the most important steps in preventing over-harvesting of the donor area is choosing the right hair transplant clinic. A reputable and experienced clinic will have the knowledge and skills to manage the donor area effectively, to ensure that the best possible results are achieved.
Estenove, located in Istanbul, Turkey, is a leading hair transplant clinic that is renowned for its expertise in managing the donor area. Estenove uses the latest techniques and technologies to ensure that each patient’s donor area is carefully managed, to prevent over-harvesting and to achieve the best possible results.
Why Choose Estenove?
There are several reasons why Estenove is the ideal choice for your hair transplant. Firstly, our clinic is staffed by a team of highly experienced surgeons and technicians, who are experts in the field of hair transplantation.
Secondly, Estenove uses the latest techniques and technologies in hair transplantation. This includes the use of automated FUE devices, which can extract individual hair follicles with precision and speed. This can reduce the risk of over-harvesting and scarring, and can improve the overall results of the transplant.
Thirdly, Turkey is known to offer a more affordable option for hair transplant surgery compared to other countries like the US, UK, and Canada. The cost of a hair transplant in Istanbul, Turkey is generally lower due to several factors, such as the lower cost of living, availability of experienced and skilled hair transplant surgeons, and the relatively low cost of running a hair transplant clinic in Turkey.
Finally, Estenove is committed to providing a high level of patient care. This includes providing a comprehensive consultation and assessment before the procedure, to ensure that the patient’s goals and expectations are fully understood. We also provide ongoing support and aftercare following the procedure, to ensure that the patient’s recovery is smooth and successful.
Conclusion
Over-harvesting of the donor area is a common issue in hair transplantation, but it can be prevented with careful planning and management. By choosing a reputable and experienced hair transplant clinic, such as Estenove, you can ensure that your donor area is managed effectively, to achieve the best possible results.
Remember, a successful hair transplant is not just about the number of hair follicles that are transplanted, but also about the health and appearance of the donor area. By understanding the risks of over-harvesting and taking steps to prevent it, you can ensure that your hair transplant is a success, both now and in the future.
Fill the form below to get free consultation